Magnesium for Depression: The Science Behind Its Effectiveness
Are you battling depression and seeking a natural solution? Magnesium for depression is emerging as a promising option, offering hope where traditional treatments may fall short.
This essential mineral, often overlooked in mental health discussions, plays a crucial role in brain chemistry.
Recent studies suggest that magnesium could significantly reduce depressive symptoms, potentially offering an affordable, fast-acting, and well-tolerated approach to managing mood disorders.
In this guide, you’ll discover how magnesium impacts brain function, explore the latest research on its effectiveness for depression, and learn practical ways to incorporate it into your mental health regimen.
Whether you’re looking for an alternative to conventional treatments or aiming to enhance your current approach, understanding the potential of magnesium for depression could be your next step towards improved mental well-being.
Key Takeaways
- Magnesium plays a crucial role in mental health by interacting with key brain receptors and enzymes, helping to regulate mood and potentially alleviate depression.
- Research, including randomized controlled trials, indicates that magnesium supplementation can significantly reduce depression symptoms, often showing quicker results compared to traditional antidepressants.
- Different forms of magnesium supplements vary in their bioavailability, with magnesium citrate and magnesium chloride being more effective due to their higher absorption rates, making them better choices for addressing magnesium deficiency and depressive symptoms.
- Full-spectrum magnesium supplements combine multiple forms of magnesium, potentially offering broader health benefits including mood support.
Understanding the Role of Magnesium in Mental Health
Magnesium is integral to our mental well-being, acting as a protective shield for our brain’s delicate balance.
This essential mineral serves as a co-factor in over 350 enzymes in the human body, many of which are vital for proper brain function.
Its importance in mood regulation cannot be overstated, as it helps to balance and control various neurotransmitters that influence our emotional state.
One of the key ways magnesium impacts our mental health is through its interaction with the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor.
By blocking the ion channel of this receptor, magnesium prevents its excessive activation and protects nerve cells from an influx of calcium.
This modulation of neurotransmission in the central nervous system supports psychiatric and neurological stability.
Additionally, magnesium’s role in modulating the central nervous system and its impact on systemic inflammation, sleep disturbances, and mood disorders can also be beneficial for postpartum depression.
A deeper look into the science behind magnesium’s effects on depression reveals how the mineral’s unique properties can potentially improve mental health outcomes.
The science behind magnesium and depression
The link between magnesium and depression stems from the mineral’s core role in brain function.
As we’ve mentioned, magnesium acts as a co-factor in more than 350 enzymes in humans, many of which are crucial for maintaining optimal brain health.
This extensive involvement in brain chemistry allows magnesium to influence mood regulation by balancing various chemical compounds in the brain.
A notable aspect of magnesium’s influence on depression is its interaction with the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor.
Magnesium is a potent antagonist of this receptor complex, which plays a significant role in regulating mood and cognitive function.
By inhibiting excessive NMDA receptor activity, magnesium helps maintain a healthy balance of neurotransmitters in the brain, potentially alleviating symptoms of depression.
Furthermore, magnesium has been shown to affect other key players in the brain’s mood regulation system.
For instance, it inhibits glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK-3), an enzyme that has been implicated in mood disorders.
Interestingly, this inhibition is similar to the action of several antidepressant medications, suggesting that magnesium may work through similar pathways to improve mood.
Several studies have conducted randomized clinical trials to assess the impact of magnesium supplements on depression, highlighting significant findings that support its effectiveness in reducing depression symptoms.
For example, a randomized clinical trial by Tarleton et al. demonstrated that magnesium supplementation could significantly alleviate depressive symptoms.
Further supporting the link between this mineral and mood disorders, research has revealed that body magnesium levels can fluctuate during depressive episodes.
Brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and magnesium
Another fascinating aspect of magnesium’s role in mental health is its relationship with brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF).
BDNF is a protein that plays a crucial role in the growth, maintenance, and survival of neurons in the brain. It’s often referred to as “fertilizer for the brain” due to its importance in cognitive function and mental health.
Interestingly, magnesium levels are closely linked to the expression of BDNF, highlighting yet another way this mineral contributes to our mental well-being.
Studies have shown that supplementing with magnesium can enhance the expression of BDNF in the brain, especially in the prefrontal cortex.
This effect is similar to that observed with ketamine, a drug that has gained attention for its rapid antidepressant effects.
The increase in BDNF expression is thought to contribute significantly to the antidepressant effects of both magnesium and ketamine.
By promoting the growth and plasticity of neurons, increased BDNF levels may help the brain adapt and recover from the neural changes associated with depression, potentially leading to improved mood and cognitive function.
Research on Magnesium Supplementation for Depression
With the potential link between magnesium and depression becoming more apparent, researchers have shifted their focus to explore the effects of magnesium supplementation on depressive symptoms.
The results have been promising, with numerous studies showing that magnesium supplementation can significantly reduce and improve depression scores.
This effect seems to be particularly pronounced when magnesium is used in combination with antidepressants, suggesting a potential synergistic effect that could enhance treatment outcomes for those struggling with depression.
Specific studies have conducted randomized controlled clinical trials to assess the impact of magnesium supplements on depression, including findings that highlight the potential benefits of adding magnesium to existing antidepressant treatments.
One compelling feature of magnesium as a potential depression treatment is its affordability, rapid action, and general tolerability.
These characteristics make it an attractive option for those seeking alternative or complementary treatments for depression.
Moreover, some researchers suggest that magnesium treatment in clinical trials could be as effective as, or even more effective than, traditional antidepressant drugs.
This potential has led to increased interest in magnesium as a treatment option, particularly for individuals who have not responded well to conventional antidepressant therapies.
Randomized controlled trials
Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have been instrumental in confirming the efficacy of magnesium supplementation for depression.
These rigorous studies offer the most reliable evidence in medical research, enabling more conclusive insights about the effects of magnesium on depressive symptoms.
Several RCTs have investigated the impact of magnesium supplements on patients with major depressive disorders, yielding valuable insights into this potential treatment approach.
One notable study examined the effects of magnesium chloride supplementation on depression scores over a six-week period.
The results were striking: participants who received magnesium chloride reported a net improvement of -6.0 points in their depression scores.
This significant reduction in symptoms suggests that magnesium supplementation could have a meaningful impact on the lives of those struggling with depression.
Another study focused on the effects of magnesium supplementation over a longer period. Researchers found that:
- The mean Beck scores (a widely used measure of depression severity) of patients in the magnesium intervention group were lower compared to the control group after just four weeks of treatment.
- This rapid improvement is particularly encouraging, as many traditional antidepressants can take several weeks to show noticeable effects.
- The study also noted that these improvements continued throughout the intervention period, with mean Beck scores decreasing further in the magnesium group compared to the placebo group by the end of the study.
Systematic reviews and meta-analyses
While individual studies offer important insights, systematic reviews, and meta-analyses broaden the perspective by amalgamating data from multiple trials.
A comprehensive meta-analysis of randomized controlled trialsinvestigating magnesium supplementation for depression has revealed some exciting findings.
The analysis, which adhered to the PRISMA protocol for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses, initially identified over 3,000 publications related to the topic, including those on selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors.
After rigorous screening, seven eligible randomized controlled trials were included in the final analysis. The results were compelling:
- The meta-analysis found that magnesium supplementation caused a significant drop in depression scores compared to placebo.
- Interestingly, a subgroup analysis suggested that lower doses of magnesium supplements (250 mg/day or less) may have a stronger effect on reducing depression scores than higher doses.
- This finding highlights the importance of proper dosing in magnesium supplementation and suggests that more isn’t always better when it comes to this mineral’s effects on mental health.
Types of Magnesium Supplements
When considering magnesium supplementation for depression, it’s important to know that not all forms of the mineral are alike.
There are several types of magnesium supplements available on the market, each with its own unique properties and potential benefits. The most common forms include:
- Magnesium oxide.
- Magnesium citrate.
- Magnesium chloride.
- Magnesium sulfate.
Understanding the differences between these supplements is important for anyone considering adding magnesium supplementation to their mental health regimen.
The key factor that distinguishes these different forms of magnesium is their bioavailability – that is, how easily they are absorbed and utilized by the body.
This factor can significantly influence the effectiveness of the supplement in addressing magnesium deficiency and potentially improving depressive symptoms.
For instance, magnesium oxide, while commonly used, has a lower bioavailability compared to other forms.
On the other hand, magnesium citrate is known for its superior absorption rate, making it a popular choice for those seeking to increase their magnesium levels effectively.
Magnesium chloride vs. magnesium sulfate
When comparing different forms of magnesium supplements, magnesium chloride and magnesium sulfate are two options that often come up in discussions about mental health.
Both have their unique properties and potential benefits, but magnesium chloride tends to stand out when it comes to oral supplementation for depression.
Magnesium chloride is often praised for its ability to replenish magnesium levels quickly due to its excellent absorption properties.
This rapid absorption makes it particularly beneficial for treating depression, as it can effectively raise magnesium levels in the body, potentially leading to faster symptom relief.
Moreover, magnesium chloride is considered superior for oral supplementation due to its high solubility, which contributes to its impressive absorption rate.
These characteristics make magnesium chloride a popular choice among those looking to address magnesium deficiency and its potential impact on mental health.
Magnesium oxide and magnesium citrate
When it comes to magnesium supplements, two forms that are frequently compared are magnesium oxide and magnesium citrate.
While both can increase magnesium levels in the body, they differ significantly in their absorption rates and overall effectiveness.
Magnesium citrate is often the preferred choice for those seeking to boost their magnesium levels due to its higher bioavailability.
This means that a larger proportion of the magnesium in this form is absorbed by the body, making it more effective at increasing overall magnesium levels.
On the other hand, magnesium oxide has one of the lowest bioavailability rates among magnesium supplements.
This lower absorption rate means that while magnesium oxide supplements may contain a high percentage of elemental magnesium, less of it actually makes its way into the body’s systems where it can have an impact on mental health.
As a result, when comparing these two supplements for their potential effects on depression, magnesium citrate generally comes out on top due to its superior ability to raise magnesium levels in the body effectively.
Full-Spectrum Magnesium Supplementation: A Comprehensive Approach
While single-form magnesium supplements can be beneficial, full-spectrum magnesium supplements offer a more comprehensive approach to addressing various aspects of health, including mental well-being.
These supplements typically combine multiple forms of elemental magnesium, each with its own unique benefits:
- Magnesium Chelate: Supports muscle recovery.
- Magnesium Glycinate: Promotes sleep, anxiety relief, and brain health.
- Magnesium Aspartate: May help with mood, anxiety, and depression.
- Magnesium Malate: Supports brain and nervous system function.
- Magnesium Orotate: Beneficial for heart health and exercise performance.
- Magnesium Taurate: May help with blood pressure and relaxation.
- Magnesium Citrate: Supports cardiovascular and intestinal health.
Many full-spectrum formulations also include co-factors that can enhance magnesium’s effectiveness:
- Vitamin B6: May improve stress reduction when combined with magnesium.
- Manganese: Supports bone strength.
Potential Benefits of a full-spectrum magnesium supplementation also include:
- Stress and anxiety reduction.
- Improved sleep quality.
- Heart and bone health support.
- Enhanced nutrient absorption and energy production.
- Healthy cellular and nerve function.
- Muscle mass maintenance and post-exercise recovery.
While these potential benefits are promising, it’s important to note that individual results may vary. As with any supplement regimen, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting.
If you’re considering a magnesium supplement to support your mental health, a full-spectrum formulation may offer a well-rounded approach.
Look for a high-quality supplement that combines various forms of magnesium with supporting nutrients for optimal results.
Dosage and Safety Considerations

When considering magnesium supplementation for depression, it’s important to understand the appropriate dosage and be aware of potential safety concerns.
The recommended daily intake of magnesium varies depending on age and gender.
The recommended daily amount of magnesium for adult men ranges between 400 and 420 mg.
For adult women, the range is between 310 and 320 mg. It’s important to note that these recommendations cover total magnesium intake from both dietary sources and supplements.
While magnesium supplementation can be beneficial for many people, it’s not without potential side effects, especially when taken in very high doses.
Some individuals may experience abdominal pain, diarrhea, or nausea if they consume excessive amounts of magnesium.
In rare cases, very high intakes could lead to heart problems.
However, it’s worth noting that in studies on magnesium supplementation for depression, no explicit side effects were observed.
This suggests that when taken within recommended doses, magnesium supplements are generally well-tolerated by most individuals.
Recommended dietary magnesium intake
Being aware of the recommended dietary intake of magnesium is key to maintaining optimal mental health and potentially easing depressive symptoms.
For adult men, the daily recommended magnesium intake is between 400 to 420 milligrams, while for adult women, it’s slightly lower at 310 to 320 milligrams per day.
These recommendations are based on extensive research and are designed to ensure that most individuals meet their basic magnesium needs through diet and supplementation if necessary.
It’s important to note that certain life stages may require adjustments to magnesium intake.
For instance, pregnant women over 18 years of age are advised to increase their magnesium intake to 350–360 mg per day to support both maternal and fetal health.
Additionally, some studies have shown potential benefits of higher magnesium intake for specific groups.
A review of three studies among older adults found that supplementing with 320 to 720 mg of magnesium daily for up to 8 weeks yielded improvements in sleep quality, which can indirectly support mental health.
This highlights the potential benefits of magnesium supplementation beyond just meeting basic nutritional needs, especially when it comes to mental health and well-being.
Potential side effects and interactions
Although magnesium supplementation can be beneficial for many people, particularly those dealing with depression, it’s important to be cognizant of possible side effects and interactions.
One of the primary concerns with magnesium supplementation is the risk of toxicity if the recommended intake is exceeded.
This underscores the importance of adhering to recommended dosages and consulting with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
The symptoms of magnesium toxicity can be uncomfortable and may include nausea, abdominal cramping, and diarrhea.
These gastrointestinal symptoms are often the first signs that magnesium intake has exceeded the body’s ability to process it effectively.
It’s worth noting that these side effects typically occur only with excessive intake, and most people can safely take magnesium supplements within the recommended dosage range without experiencing adverse effects.
However, to ensure safety and maximize the potential benefits for mental health, it’s crucial to adhere to the recommended dosages of magnesium and to consult with a healthcare professional, especially if you’re taking other medications or have existing health conditions.
Practical Tips for Increasing Magnesium Intake
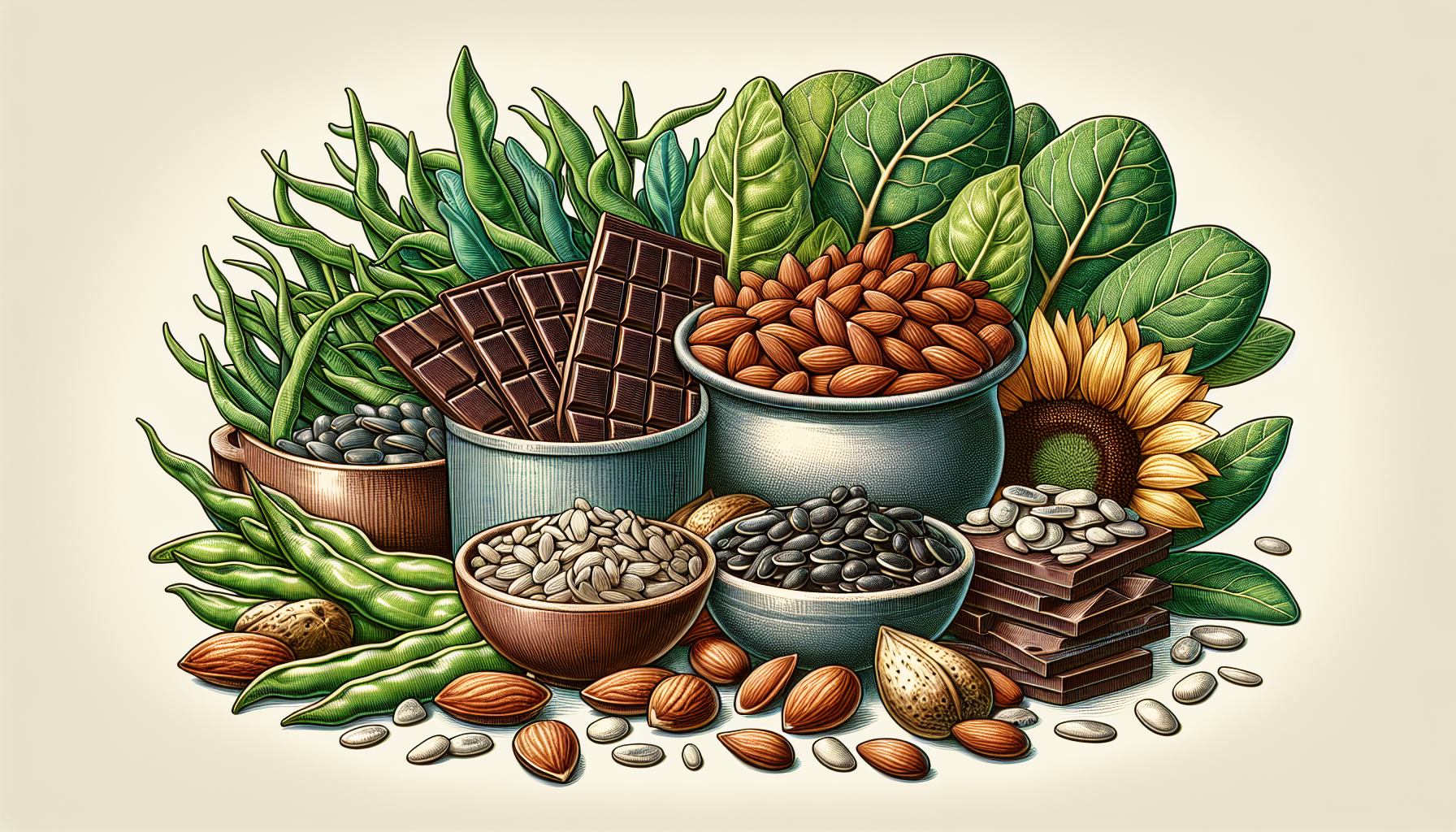

Boosting your magnesium intake isn’t synonymous with relying solely on supplements.
In fact, one of the most effective and natural ways to boost your magnesium levels is through dietary changes.
Incorporating more magnesium-rich foods into your daily meals can significantly contribute to meeting your recommended intake. Some examples of magnesium-rich foods include:
- Leafy greens.
- Nuts.
- Seeds.
- Whole grains.
- Beans.
By making conscious choices to include these foods in your diet, you can support your mental health while also enjoying a diverse and nutritious range of foods.
For those who struggle to meet their magnesium needs through diet alone, or for individuals with increased magnesium requirements, supplementation can be a beneficial option.
However, choosing the right supplement is crucial for maximizing the potential benefits. Factors such as bioavailability, form of magnesium, and individual health needs should all be considered when selecting a magnesium supplement.
In the following sections, we’ll explore both dietary sources of magnesium and tips for choosing the most suitable supplement to support your mental health journey.
Dietary sources of magnesium
Incorporating magnesium-rich foods into your diet is a delicious and natural way to boost your intake of this essential mineral.
Nature provides us with an abundance of magnesium sources, many of which can be easily integrated into our daily meals. Some of the best dietary sources of magnesium include:
- Nuts.
- Seeds.
- Leafy green vegetables.
- Beans.
- Dark chocolate.
Let’s explore some specific foods and their magnesium content to help you make informed choices about your diet.
Seeds are particularly rich in magnesium.
Pumpkin seeds, for instance, are a magnesium powerhouse, providing an impressive 168-156 milligrams of magnesium per ounce.
Chia seeds are another excellent option, offering 111 milligrams of magnesium per ounce.
Nuts are also a great source of magnesium, with almonds containing 80 milligrams per ounce and cashews providing 74 milligrams per ounce.
Leafy green vegetables are not only packed with various vitamins and minerals but are also rich in magnesium. Some examples include:
- Half a cup of boiled spinach contains 78 milligrams of magnesium.
- Legumes like black beans provide 60 milligrams of magnesium per half cup when cooked.
- Dark chocolate with 60-69% cocoa content contains about 50 milligrams of magnesium per ounce.
By incorporating a variety of these foods into your diet, you can significantly boost your magnesium intake and potentially support your mental health in a natural and enjoyable way.
Choosing the right supplement
While getting magnesium through diet is ideal, there are times when supplementation is necessary to meet your body’s needs, particularly when dealing with mental health issues like depression.
When choosing a magnesium supplement, it’s important to understand that not all forms are created equal.
The market offers various types of magnesium supplements, including:
- Magnesium chloride
- Magnesium sulfate
- Magnesium oxide
- Magnesium citrate
Each of these forms has different properties that affect how well they are absorbed and utilized by the body.
The absorption rate, or bioavailability, of a magnesium supplement is a crucial factor to consider. For instance, magnesium chloride and magnesium sulfate have different absorption rates, which can impact their effectiveness for specific health conditions, including depression.
Similarly, magnesium oxide and magnesium citrate vary in their bioavailability, which can influence their efficacy in treating depressive symptoms.
Generally, magnesium citrate and magnesium chloride are often recommended due to their higher absorption rates.
However, the best choice may vary depending on individual factors such as your specific health needs, any existing medications you’re taking, and your doctor’s recommendations.
It’s always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen, especially when it’s intended to support mental health.
Summary
Magnesium plays a vital role in mental health, particularly in managing depression.
Scientific evidence supports its potential to alleviate depressive symptoms through various mechanisms, including neurotransmitter regulation and BDNF production.
While dietary sources are beneficial, supplementation may be necessary for optimal results.
Full-spectrum magnesium supplements offer a comprehensive approach, combining different forms of magnesium to address various aspects of mental and physical health. These supplements may provide broader benefits compared to single-form options.
If you’re considering magnesium for depression management, consult with a healthcare professional about incorporating a high-quality, full-spectrum magnesium supplement into your routine.
This natural approach could be a valuable addition to your mental health strategy, potentially offering relief and improved well-being.
Take action today: Explore full-spectrum magnesium supplements and take a step towards better mental health.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take for magnesium supplements to start working for depression?
It may take around 2-4 weeks to see improvements in depression scores after starting magnesium supplementation, but consistency in taking the supplement and maintaining proper dosage is crucial for potential benefits.
Can magnesium supplements interact with antidepressant medications?
Yes, magnesium supplements can potentially interact with certain antidepressant medications, so it’s important to consult with your healthcare provider before taking them together to ensure safety and avoid potential interactions.
What’s the best form of magnesium supplement for depression?
The best form of magnesium supplement for depression can vary depending on individual factors.
Magnesium citrate and magnesium chloride are often recommended due to their higher absorption rates, but it’s best to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable form for your specific needs.
Are there any side effects of taking magnesium supplements for depression?
Yes, there can be some side effects of taking magnesium supplements for depression, such as diarrhea, nausea, or abdominal cramping, especially at higher doses.
If you experience any adverse effects, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider.
Can I get enough magnesium from my diet alone to help with depression?
In conclusion, while it’s possible to get magnesium from your diet, many people don’t get enough solely from food, so supplementation may be necessary for managing depression.
Always seek advice from a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.



Comments