Empowering you Organically – Season 2 – Episode 15
Title: Collagens: Hype or Healthy?
Hosts: Jonathan Hunsaker & TeriAnn Trevenen
Guest: None
Description: The search term collagen has increased 40% already just in this year alone! So, is all the hype trendy or true? We’ve done the research and that’s the question we answer this week!
Powerful Proteins Help Smooth Wrinkles, Keep Skin Plump, and Promote Joint Health
- FOUR COLLAGEN SOURCES: We’ve combined collagen types I, II, III, V and X – the major types of collagen your body needs – from four different sources (grass-fed cows, wild-caught fish, antibiotic-free chicken, eggshell membrane) for the ultimate matrix of health benefits.
- HIGHLY BIOAVAILABLE: Clean Sourced Collagen is formulated with VItamin C, Horsetail Extract and Zinc for maximum absorption.
- EASY TO TAKE: Our revolutionary, odorless, tasteless, and easy-to-mix Clean Sourced Collagens can be added to a wide variety of healthy foods or mixed into water, juice, or your favorite smoothie.
- NATURAL INGREDIENTS: We only use the purest ingredients found on Earth and our supplements are free from artificial flavors, preservatives, colors, yeast, soy protein, sodium, starch and are non-GMO.
Did you know that your body naturally produces collagen every day? We dig into why supplementation is even a consideration.
Did you know there are several different types of collagen? We’ve tracked them all down and explain the part each type plays in our body.
Is collagen all about less sagging skin? Actually, no it isn’t! Tune in to hear about the ways collagen benefits our health. We guarantee some will surprise you.
Tune in for more no-nonsense information on what collagens are, how they may benefit your health, and what you need to look for when it comes to the products and foods, you’re consuming.
What is collagen?
Dictionary result for collagen
/ˈkäləjən/
noun
- the main structural protein found in skin and other connective tissues, widely used in purified form for cosmetic surgical treatments.
- “vitamin C plays a vital role in the formation of collagen”
- Different collagen molecules make up about ⅓ of the total protein in a human body
- Found in bone, skin, muscles, and tendons
- The substance that connects cells and gives skin elasticity as well as strength
Collagen and Aging
- Your body naturally produces collagen every day.
- After the age of 25, we break down more collagen than we make.
- Collagen supplements are an easy way to add more collagen to your diet.
- Collagen has been shown to reduce wrinkles, keep joints strong and flexible, support strong bones, and increase skin hydration.
Why is collagen so good for you?
Collagen is vital for maintaining the structure and integrity of your entire body.
#1 – Strong Cartilage and Muscles
- Cartilage is a type of connective tissue that is made up of collagen When you lack collagen, joint instability, stiffness, and pain can result. Likewise, muscles need cartilage to adhere themselves to the ends of bones. This is why muscle aches are one of the most common complaints of individuals with low collagen levels.
#2 – Healthy Teeth.
- Collagen is needed to keep teeth in place in the gums. Loose teeth, toothache, sensitive teeth, and even tooth loss can result from a lack of collagen overall.
#3 – Thick Hair
- Collagen plays an important part in hair growth since it fills in the spaces around each hair follicle. One way to tell if you are collagen deficient is to notice the quality and state of your hair. Dull, thin hair is a sign of low collagen levels. Collagen also helps fight free radicals that can damage hair.
#4 – Smooth Skin
- Wrinkling and cellulite are other unfortunate results of low collagen in the body. Not enough collagen means skin begins to lose elasticity and sag, causing those pesky wrinkles as we age. Cellulite is another telltale sign of low collagen.
#5 – Good Gut Health.
- Collagen helps heal the gut because of its ability to “seal the gut.” Leaky gut has been linked to autoimmune conditions and neurological conditions like autism.
Types of Collagens
There are over two dozen kinds of collagen, although roughly 85% of the collagen in the body is made up of Type I, II, or III (or a combination of these three types).
- Type I collagen is the most prevalent type of collagen. It is the substance that makes up the skin, tendons, and bones as well as the structural framework of the organs. It should be your go-to for hair, skin, and nail health, especially for recouping lost collagen stores that occurs naturally as we age. It is also a “well-rounded generalist,” in that it is a good type for supporting overall health. Type I is also found in the digestive tract, which makes it (along with Type II) great for gut healing and repair.
- Type II collagen is the structural component of cartilage in the body. Because of this, it is great for the joints and to rebuild cartilage in ligaments, tendons, skin, and bones. Type II collagen contains a variety of specific amino acids that are particularly helpful for the body. The first one, again, is glycine, which is beneficial for brain health and metabolism. The second one is proline, which helps clean artery walls. Type II may also be good for the respiratory system, detoxification pathways, and more because it contains arginine, another amino acid that is vital for nitric oxide production. [Note: Nitric oxide is produced in the body and is beneficial for supporting blood flow and lowering blood pressure.] For the most part, Type II collagen is where you want to turn for joint health and possibly even for arthritis support.
- Type III collagen is typically found where ever Type 1 collagen can be found as well as some other unique places. It is housed in what are called reticular fibers, the substances that make up connective tissue. It is also found in the muscles, bone marrow, blood vessels, and reproductive organs such as the uterus. Type III collagen is also crucial for the healthy functioning of the cardiovascular system. Low Type III collagen has been linked to ruptured blood vessels and can be life-threatening.
- Type IV collagen helps to strengthen endothelial cells that form the tissue protecting organs as well as muscles and fatty tissue. Endothelial cells also line the majority of the surfaces along the digestive tract and respiratory organs.
- Type V collagen helps create the surface of cells while Type X helps with bone formation. There are at least a dozen others, all doing their job to keep your body lubricated, moving, and functioning at its best.
How to Help Your Body Create Collagen Naturally
- Eat a diet and live a lifestyle that promotes the healthy synthesizing of your own natural healing and repair mechanisms
- Avoid UV radiation exposure
- Do not smoke cigarettes
- Reduce/Manage stress levels
What To Look For In A Collagen Supplement
- Look for multiple types of collagens
- Clean sourced and organic
- Bio-Availability – what is the delivery system – fermented, sprouted
- Whole food and not synthetic ingredients
- Contains Vitamin C – Without adequate amounts of dietary vitamin C, the body can’t actually form or store collagen
- Be sure the manufacturer does consistent batch testing for heavy metals
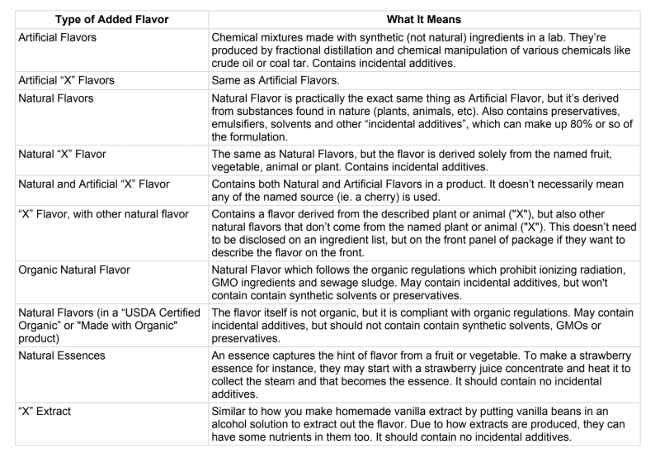
- Watch out for Natural Flavoring
Ingredient List for Organixx Clean Sourced Collagens, Multi-Collagen Blend:
- Hydrolyzed Grass Fed Pasture-Raised Bovine Collagen Peptides,
- Bovine Bone Broth Hydrolyzed Protein,
- Chicken Bone Broth Collagen Concentrate,
- Clean Marine® Wild Caught Hydrolyzed Fish Collagen Peptides,
- Eggshell Membrane Collagen,
- Acerola Cherry (natural source of Vitamin C),
- Camu Camu (natural source of Vitamin C),
- Silica from Organic Horsetail,
- Zinc Gluconate,
- Fulvic Acid,
- and Pyroxidine Hydrochloride (Vitamin B6).
Natural Flavors – Buyer Beware
Important to note, a governmental or independent agency does not approve or oversee the safety of the food flavors.
Studies:
A randomized, double-blind, multicenter, controlled clinical trial of chicken type II collagen in patients with rheumatoid arthritis– To assess the efficacy and safety of chicken type II collagen (CCII) in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) compared with methotrexate (MTX).
CONCLUSION: CCII is effective in the treatment of RA. CCII is well tolerated, and the incidence of adverse events of CCII is lower than that of MTX.
Effect of Orally Administered Collagen Peptides from Bovine Bone on Skin Aging in Chronologically Aged Mice – In summary, the present study demonstrated oral administration of collagen peptides from bovine bone could improve the laxity of chronologically aged skin by increasing skin collagen content and ratio of type I to type III collagen, but it had no effect on moisture retention of skin.
An Overview of the Beneficial Effects of Hydrolysed Collagen as a Nutraceutical on Skin Properties: Scientific Background and Clinical Studies – Skin, the main barrier to the external environment, is subject to deterioration caused by dermatological disorders, environmental conditions, and the intrinsic aging process. This damage to both structure and function may be accelerated by smoking, alcohol consumption and chronic sun exposure (extrinsic components). All these factors may lead to the formation of wrinkles, the appearance of brown spots and skin thickening. One effective strategy to managing the skin aging process is adopting a healthy nutritional approach to life, maintaining a balanced diet and a good supply of food supplements. This can restore the homeostasis of macro and micronutrients and support the physiology of cells and tissues in the skin. Hydrolyzed collagen, an increasingly popular nutraceutical, is composed of low molecular weight small peptides, which are easily digestible, absorbed and distributed in the human body. Numerous clinical trials have now been performed showing the efficacy and benefits of collagen peptides on skin properties, such as hydration, elasticity, and reduction of wrinkles. As a result, hydrolyzed collagen can be considered an important weapon in the everyday fight against skin aging.
Dietary Supplementation with Specific Collagen Peptides Has a Body Mass Index-Dependent Beneficial Effect on Cellulite Morphology – The results obtained in this study demonstrated that oral supplementation with specific BCP over a period of 6 months led to a clear improvement of the skin appearance in women suffering from moderate cellulite. In addition, the data showed the marked potential of BCP to improve the skin morphology of cellulite-affected areas, providing new evidence of BCP’s beneficial effects and postulating a new therapy strategy for cellulite treatment.
24-Week study on the use of collagen hydrolysate as a dietary supplement in athletes with activity-related joint pain. – The results of this study have implications for the use of collagen hydrolysate to support joint health and possibly reduce the risk of joint deterioration in a high-risk group.
* * *
Subscribe to Empowering You Organically
Never miss an episode!
APPLE PODCASTS SPOTIFY GOOGLE PODCASTS
–
Episode 15 – Title: Collagens: Hype or Healthy?





