Are you magnesium deficient? Constant fatigue, muscle cramps, and heart palpitations might be telling you something. This crucial mineral, often overlooked, powers over 300 bodily functions.
Up to 75% of Americans don’t get enough magnesium, impacting everything from energy levels to nerve function. Imagine feeling vibrant and cramp-free, with a steady heartbeat.
Discover the top symptoms of magnesium deficiency, its causes, and simple solutions in this guide. It’s time to unlock your health potential through optimal magnesium levels.
Key Takeaways
- Magnesium is vital for energy production, nerve function, and blood sugar control.
- Common deficiency symptoms include muscle cramps, fatigue, and cardiovascular issues.
- Diagnosis involves symptom evaluation and blood tests; treatment includes dietary changes and supplements.
- Full-spectrum magnesium supplements, combining multiple forms of magnesium, can offer comprehensive benefits and improved absorption.
Understanding Magnesium Deficiency
A deficiency in magnesium arises when an individual’s diet does not supply a sufficient amount of this essential mineral for normal bodily functions.
Magnesium is integral to numerous biochemical reactions, playing a pivotal role in the overall maintenance of health. Its various crucial functions include:
- energy production from food,
- regulation of the nervous system,
- protein synthesis,
- maintaining muscle and nerve function at optimal levels,
- controlling blood sugar balance,
- and boosting immune health.
The question “how much magnesium should one take?” frequently comes up as people strive to ensure they are getting enough magnesium to meet their body’s needs.
To fill any gaps in dietary intake of this mineral and reach recommended daily amounts may prompt consideration towards using a magnesium supplement.
Magnesium reserves are mainly stored within our bones, which act as a reservoir that can be utilized if dietary sources become insufficient.
The kidneys also play an important role by regulating how much magnesium the body retains.
Low concentrations can trigger several health problems such as high blood pressure (hypertension), type 2 diabetes, and bone weakening conditions like osteoporosis.
Older individuals often experience heightened risk for depleted levels of magnesium due to factors including lower consumption through diet diminished absorption efficiency, and increased loss via renal excretion.
Thus, being low on magnesium for a long time can lead to serious health problems like heart disease, diabetes, and migraines.
It’s important to understand how vital magnesium is and to watch for signs of deficiency to maintain your best health.
Common Symptoms Magnesium Deficient People May Experience

Symptoms of magnesium deficiency can be subtle and might resemble various other health conditions, leading to confusion.
These signs, including muscle cramps, spasms, fatigue, and cardiovascular problems, must be identified early to avert the potential development of long-term health issues related to insufficient magnesium levels.
Muscle Cramps and Spasms
Muscle cramps and spasms are often indicative of low magnesium levels, with nighttime leg cramps being a significant symptom.
Should the deficiency be severe, it can lead to seizures or convulsions, underscoring the importance of quickly correcting low magnesium levels in the body.
Fatigue and Weakness
Consistently experiencing fatigue and muscle weakness could be a sign that you are suffering from more than just insufficient sleep.
A deficiency in magnesium can disrupt nerve communication and affect the potassium concentration within muscle cells, contributing to these symptoms.
Although these indicators are not unique to a lack of magnesium, their presence alongside other related signs should serve as a warning signal for potential magnesium deficiency.
Cardiovascular Issues
Heart health is intimately connected to the magnesium content in one’s body.
A deficiency in this vital mineral may result in arrhythmia and heart palpitations, which can increase the likelihood of suffering a stroke or cardiac failure.
Should you notice irregular heartbeat patterns or other related cardiovascular issues, it might be prudent to investigate low magnesium as a potential root cause.
Causes of Low Magnesium Levels
Magnesium deficiency can arise from numerous sources, such as:
- Specific health conditions.
- Various medications.
- Inadequate dietary consumption.
- Long-standing medical issues.
- Particular drugs.
Identifying these key factors is crucial for the proactive prevention of low magnesium levels.
Understanding what leads to low magnesium enables you to actively prevent a deficiency in this nutrient.
Poor Dietary Intake

Numerous current diets do not supply sufficient amounts of magnesium.
Data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) indicate that almost half of the population in America does not consume enough magnesium to meet the estimated average requirement, suggesting a widespread potential for magnesium deficiency.
The shortfall in consuming foods abundant with magnesium – including nuts, seeds, green leafy vegetables, and whole grains – is a notable contributor to the risk of insufficient magnesium intake.
Chronic Health Conditions
Individuals with long-standing health conditions, especially those affecting the gastrointestinal tract such as Crohn’s disease and celiac disease, may experience compromised absorption of magnesium.
Those suffering from diabetes or alcohol use disorder, as well as individuals who have had gastrointestinal surgeries, face a heightened risk of developing magnesium deficiency because their conditions can lead to inadequate absorption or augmented excretion of this mineral.
Certain Medications
Particular medications, including diuretics and notably proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), may lead to a reduction in magnesium levels within the body.
Extended usage of PPIs, which are frequently employed for acid reflux management, can result in hypomagnesemia and thus require regular monitoring of magnesium levels.
Conversely, diuretics elevate the excretion rate of magnesium through urine, thereby playing a role in causing deficiencies.
Diagnosing Magnesium Deficiency
To accurately diagnose a deficiency in magnesium, one must use an array of diagnostic techniques including evaluating symptoms, utilizing blood tests, and employing advanced testing procedures.
This is essential because relying solely on blood tests may not yield dependable results.
Hence, all potential methods should be taken into account for a precise evaluation.
Symptoms Evaluation
Identifying symptoms promptly is crucial for the timely diagnosis of magnesium deficiency. Typical indications of this condition include:
- Exhaustion.
- Muscle twitches.
- Vomiting sensation.
- Psychological health problems such as nervousness and melancholy.
Should these signs be present, it’s advisable to seek a thorough assessment from a medical professional.
Blood Test Limitations
Blood tests frequently assess magnesium levels. These evaluations may not always be accurate.
Given that merely around 1% of the body’s total magnesium content is present in the bloodstreams, standard blood level readings can fail to represent an actual deficiency accurately.
This situation underscores the importance of developing more thorough diagnostic techniques for assessing magnesium levels.
Advanced Testing Methods
Sophisticated diagnostic techniques, including magnesium RBC tests and urine magnesium tests, provide a more precise evaluation of one’s magnesium levels.
By analyzing the amount of magnesium in red blood cells and tissues, these methods deliver a better understanding of an individual’s actual status regarding this mineral.
Engaging with a healthcare professional can aid in identifying the most suitable testing method to accurately ascertain your body’s magnesium condition.
Effective Treatments for Magnesium Deficiency
Addressing magnesium deficiency treated requires a comprehensive strategy that incorporates altering one’s diet, consuming oral supplements, and administering intravenous magnesium for acute cases.
Understanding these treatment methods is crucial in effectively remedying and preventing future occurrences of magnesium deficiency.
Dietary Changes
Incorporating foods high in magnesium into your diet is an effective strategy to combat and prevent a deficiency.
Foods such as leafy greens, nuts, and whole grains are packed with magnesium and can contribute to a well-rounded healthy diet.
Adopting these dietary adjustments has the potential to significantly enhance both your levels of magnesium and your general health.
Oral Magnesium Supplements
Magnesium citrate and magnesium glycinate are types of oral magnesium supplements that successfully restore magnesium levels.
Known for its superior bioavailability, magnesium citrate is particularly effective, whereas the calming effects and high absorbency of magnesium glycinate make it a favored choice.
Employing these supplements can proficiently resolve issues related to low levels of magnesium.
Intravenous Magnesium
When an individual is faced with severe magnesium deficiency, administering magnesium intravenously may be required.
This approach offers a rapid remedy for critically low levels of magnesium and is carried out in a healthcare environment.
The delivery of IV magnesium guarantees the immediate provision of this essential mineral to the body, ensuring there are no delays in addressing low magnesium conditions.
The Benefits of Full-Spectrum Magnesium Supplements
While dietary changes can significantly improve magnesium intake, some individuals may benefit from a full-spectrum magnesium supplement.
These supplements typically combine different forms of magnesium to maximize absorption and provide a range of health benefits.
A full-spectrum magnesium supplement like Magnesium 7 can offer several advantages:
- Comprehensive coverage: By including multiple forms of magnesium, these supplements can support various bodily functions more effectively than single-form supplements.
- Enhanced absorption: Different magnesium forms are absorbed and utilized by the body in unique ways. A full-spectrum approach ensures better overall absorption and bioavailability.
- Targeted benefits: Various magnesium forms may have specific health benefits. For example, magnesium glycinate may support sleep and relaxation, while magnesium malate could aid in energy production.
- Convenience: Instead of taking multiple individual magnesium supplements, a full-spectrum option provides a convenient all-in-one solution.
- Balanced approach: Full-spectrum supplements often provide a balanced ratio of different magnesium forms, which can be challenging to achieve through diet alone.
While Magnesium 7 is one option in this category, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen. They can help determine if a full-spectrum magnesium supplement is appropriate for your individual needs and health goals.
Enhancing Magnesium Absorption
To maintain optimal magnesium levels, it’s crucial to address factors that impede its absorption.
This can be accomplished through lifestyle changes and ensuring a balance of other nutrients that facilitate the uptake of magnesium.
Balancing Other Nutrients
Maintaining a balanced intake of nutrients like vitamin D and the B-vitamin complex can markedly boost the absorption of magnesium.
Vitamin D aids in increasing magnesium uptake by the intestines, while B-vitamins enhance its absorption at a cellular level.
By ensuring that these essential nutrients are consumed in proper amounts, you can improve your body’s efficiency in utilizing magnesium.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Adjusting one’s lifestyle by decreasing the intake of alcohol, and cutting down on coffee and soda consumption can boost the body’s magnesium absorption.
Regular exercise also plays a significant role in increasing the efficiency with which the body absorbs and makes use of magnesium.
Implementing these modifications can contribute to improved levels of magnesium as well as enhance general health.
Foods High in Magnesium

Ensuring your diet includes foods abundant in magnesium is crucial to staving off a deficiency of this mineral.
Foods particularly rich in magnesium encompass various nuts and seeds, including almonds, cashews, and peanuts.
Legumes such as black beans along with grains like quinoa—and leafy vegetables such as spinach and kale—are substantial sources.
There’s an array of dietary options teeming with magnesium.
- Abundant whole grains.
- Magnesium-packed fruits like bananas and dried figs.
- Protein-rich tofu.
- Nutrient-dense yogurt.
Incorporating these diverse food items into your meal regimen can be instrumental in sustaining optimal levels of magnesium that bolster overall well-being.
Risks of Too Much Magnesium
Ensuring that you receive a sufficient amount of magnesium is crucial, but it’s equally critical to prevent ingesting too much.
High levels of magnesium consumption, often from antacids and laxatives, may lead to toxicity. This condition can manifest through various symptoms like:
- vomiting,
- lethargy,
- abdominal pain,
- and loose stools.
In the most extreme situations, an overdose of magnesium might cause severe respiratory problems and other serious health complications.
The groups most vulnerable include infants, people with kidney issues, and elderly individuals. Hence they should be vigilant in monitoring their intake of this mineral.
Magnesium and Bone Health
An adequate intake of magnesium is crucial for the synthesis of the bone matrix and the formation of bones, which are fundamental to maintaining strong bones and preventing osteoporosis, especially in older adults.
By consuming enough magnesium, you can enhance your bone mineral density and lower your risk of fractures. It’s important for supporting overall bone health and averting conditions associated with weakened bones.
Summary
Magnesium is a crucial mineral supporting various bodily functions, from muscle and nerve health to bone formation.
Recognizing the symptoms of magnesium deficiency, understanding its causes, and knowing how to diagnose and treat it are essential steps in maintaining optimal health.
By making dietary changes, considering supplements, and enhancing magnesium absorption, you can ensure your body gets the magnesium it needs.
If you are looking to optimize your magnesium intake, consider trying a full-spectrum daily magnesium supplement.
These comprehensive formulations can provide a balanced approach to addressing potential deficiencies and supporting overall health.
Consult with your healthcare provider to determine if a full-spectrum magnesium supplement is right for you and take the first step towards better magnesium balance today.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the early signs of magnesium deficiency?
If you’re experiencing muscle cramps, fatigue, and heart palpitations, it could be an early sign of magnesium deficiency.
Keep an eye for these symptoms and consider consulting a healthcare professional if you notice them.
How can I increase my magnesium intake?
To boost your magnesium levels, consider adding foods high in magnesium such as nuts, leafy greens, and whole grains to your meal plan.
Doing so can assist you in achieving the recommended daily intake of magnesium.
Are blood tests reliable for diagnosing magnesium deficiency?
Blood examinations may not be an accurate indicator for diagnosing magnesium deficiency, as they only evaluate a minimal fraction of the body’s overall magnesium content.
For a more precise evaluation, it is advisable to employ alternative diagnostic techniques.
What are the risks of taking too much magnesium?
Consuming excessive magnesium may result in indications such as diarrhea, drowsiness, and nausea. In instances of extreme overconsumption, it could potentially lead to a condition known as magnesium toxicity.
It is important to monitor your intake of magnesium attentively!
How does magnesium support bone health?
Magnesium is essential for maintaining bone health as it has a pivotal function in the formation of bones and aids in staving off osteoporosis.
Should I Be Taking Magnesium? Benefits, Risks, and GuidelinesAre you constantly tired, experiencing muscle cramps, or mood swings? You might be asking yourself, “Should I be taking magnesium?” This essential mineral plays a key role in hundreds of bodily functions, yet many people are unknowingly deficient.
From promoting better sleep to supporting heart health and even potentially warding off migraines, magnesium’s benefits are both diverse and impressive. But before you start supplementing, it’s crucial to understand the pros and cons.
This guide will explore the benefits of magnesium, potential risks, and help you decide if supplementation is right for you.
Read on to discover if this mineral could be the missing piece in your health puzzle.
Key Takeaways
- Magnesium is essential for various bodily functions, including enzyme activity, DNA synthesis, and blood pressure regulation.
- Magnesium deficiency is more common in individuals with specific health conditions like diabetes and alcohol use disorder, though it is generally rare in the overall population.
- Full-spectrum magnesium supplements combining multiple forms of the mineral may offer comprehensive benefits for various bodily functions.
- Magnesium supplements can be beneficial for lowering blood pressure, easing constipation, preventing migraines, and supporting a healthy pregnancy, but they should be taken cautiously to avoid potential side effects or interactions with medications.
Importance of Magnesium in the Body

Every cell within the human body contains magnesium, an essential ion that plays a crucial role in numerous cellular activities.
Magnesium is vital for maintaining stability in polyphosphate compounds, which are integral to the synthesis of DNA and RNA.
Insufficient levels of magnesium can interrupt these core processes, potentially triggering various health complications.
The mineral serves as a cofactor for more than 300 enzymes that either use or create ATP – the primary molecule used by cells for energy.
Beyond its cellular functions, magnesium is also key to managing blood sugar levels and controlling blood pressure.
This mineral assists mitochondria function effectively in producing energy while also regulating neurotransmitters related to sleep patterns thus contributing to improved quality and length of restful sleep periods.
Magnesium also works hand-in-hand with vitamin D. Their combined action significantly benefits bone strength and immune response among other physiological systems.
An adequate intake of this critical nutrient through diet or supplementation can greatly support these important aspects of good health.
Ensuring sufficient dietary magnesium intake can help prevent health conditions, such as:
- constipation,
- preeclampsia,
- migraines,
- mood disorders,
- high blood sugar,
- high blood pressure,
- insomnia,
- leg cramps,
- and dementia.
Ensuring adequate magnesium intake is crucial for maintaining overall well-being, as deficiencies can have significant health implications.
This underscores the importance of not underestimating the role of magnesium in nutrition and its impact on longevity and vitality.
Next, we will explore the prevalence of magnesium deficiencies, their implications for individual health, and strategies to address these nutrient shortages.
How Common is Magnesium Deficiency?
Dietary surveys in the United States consistently reveal that many individuals consume less magnesium than recommended.
Data analysis from the 2013-2016 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) indicates that 48% of Americans across all age groups do not meet the recommended magnesium intake through their diet.
People with chronic conditions like diabetes or gastrointestinal issues that affect magnesium absorption are particularly at risk.
Chronic drinking poses another major factor contributing to a potential lack of sufficient magnesium intake.
Regular consumption of alcohol may hinder absorption and boost renal excretion of magnesium, leading gradually to diminished stores over time.
Since symptoms related to insufficient magnesium levels are often mild and go undetected until they reach acute lows, it remains a frequently overlooked condition.
For most people who consume a varied diet abundant in nutrients. Deficiencies in their level of bodily magnesium hardly ever occur.
Nevertheless, individuals grappling with poor eating habits or particular health challenges must be vigilant about their consumption levels of this vital nutrient because ensuring an adequate amount through one’s food could prevent shortages while promoting overall wellness.
We’ll proceed by examining how incorporating supplemental sources might offer various positive outcomes for health issues tied to deficits when natural dietary practices don’t suffice for proper maintenance—or restoration—of normal bodily reserves.
Health Benefits of Magnesium Supplements
Taking a magnesium supplement can have a wide array of health advantages, particularly for those with specific conditions or deficiencies.
Among its most significant benefits is the capacity to decrease high blood pressure, including diastolic blood pressure.
This reduction is crucial since elevated diastolic pressure poses a major risk factor for heart disease. Magnesium supports this by inducing vascular relaxation, which enhances circulation and lowers hypertension.
Magnesium supplements may also reduce blood pressure levels, reduce the risk of heart disease, and benefit blood sugar management.
Magnesium also proves beneficial in addressing constipation and acid reflux issues due to its:
- Laxative quality that facilitates smoother bowel movements.
- Property as an antacid that counteracts excess stomach acid, alleviating digestive unease.
It’s advantageous for migraine sufferers. Research indicates these individuals often exhibit decreased magnesium levels and supplementation may prevent or treat severe headaches.
Choosing a supplement that contains a well-absorbed form of magnesium, such as magnesium citrate, can help meet daily magnesium needs and maintain overall health.
Pregnant women can benefit significantly from taking magnesium supplements. These supplements are known to alleviate common pregnancy-related issues such as migraines, heightened anxiety, leg muscle cramps, digestive difficulties, and gestational hypertension.
Additionally, magnesium intake may reduce the likelihood of preterm labor and early childbirth, as well as lower maternal serum glucose levels, potentially decreasing the risk of developing gestational diabetes.
Magnesium supplements have been shown to effectively reduce inflammation markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and interleukin-6, promoting overall wellness and potentially lowering the risk of chronic diseases.
For women, in particular, magnesium can alleviate various PMS symptoms, including bloating, depressive moods, and nervous tension.
The Benefits of Full-Spectrum Magnesium Supplementation
When considering magnesium supplementation, it’s worth exploring full-spectrum options that provide multiple forms of this essential mineral.
One such product, Magnesium 7, offers a comprehensive approach by combining seven different types of elemental magnesium along with important co-factors.
Full-spectrum magnesium supplements can provide a range of benefits due to the varied absorption rates and specific functions of different magnesium forms. For example:
- Magnesium chelate may support muscle recovery.
- Magnesium glycinate could aid sleep and brain health.
- Magnesium aspartate might help with mood regulation.
- Magnesium malate is thought to benefit the nervous system.
- Magnesium orotate may support heart health and exercise performance.
- Magnesium taurate could assist with relaxation and blood pressure regulation.
- Magnesium citrate may contribute to cardiovascular and intestinal health.
Additional co-factors like Vitamin B6 and manganese can enhance the overall effectiveness of the supplement.
For instance, research suggests that combining magnesium with Vitamin B6 may improve stress reduction.
The potential benefits of a full-spectrum magnesium supplement include:
- Stress and anxiety reduction.
- Improved sleep quality.
- Support for heart and bone health.
- Enhanced nutrient absorption and energy production.
- Healthy cellular and nerve function.
- Maintenance of muscle mass and relief for sore muscles.
While individual needs vary, those looking to optimize their magnesium intake might consider exploring a full-spectrum daily magnesium supplement.
As always, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen to ensure it’s appropriate for your specific health needs and goals.
Should Healthy Adults Take Magnesium Supplements?
Those in good health without a confirmed magnesium deficiency may ponder whether there’s any merit to including magnesium supplements as part of their routine.
Although the daily intake of such supplements is widely considered safe for most people when adhering to appropriate dosage levels, it’s crucial to evaluate if supplementation is actually needed.
Kidneys have the capacity to flush out excess magnesium effectively, which makes an overdose unlikely among healthy individuals.
There isn’t solid proof that supports significant advantages from taking magnesium supplements for adults who don’t lack this nutrient in their bodies.
The existing research has not yet convincingly shown positive effects on fatigue and mood-related symptoms, indicating possible inefficacy in these areas.
Therefore, before beginning any kind of supplement regimen, speaking with one’s doctor is imperative.
They can assess your complete medical history along with any current medication regimens you are on, helping decide if adding a supplement would be beneficial.
When contemplating oral magnesium supplementation, recognizing what constitutes a harmless amount of consumption becomes paramount.
For the majority of grown-ups, ingesting less than 350 mg per day could normally pose no safety concerns.
Exceeding this limit could lead to adverse effects, particularly for those with kidney disease. It’s crucial to monitor intake and stay within the recommended dietary limit, which is generally around or below 400 mg daily.
Safety and Risks of Magnesium Supplementation
Utilizing magnesium supplements is widely considered harmless when taken in appropriate amounts.
For the majority of adult individuals, daily oral doses below 350 mg are deemed to be within a safe limit.
Nevertheless, as with all supplements, ingesting magnesium may lead to certain adverse reactions. Some of the common side effects associated with this supplement include:
- upset stomach,
- feelings of nausea,
- episodes of vomiting,
- and bouts of diarrhea.
These issues might manifest during your course of treatment and are usually mild and controllable. It’s critical to recognize their potential occurrence.
Consuming too much magnesium can result in severe health issues.
Although uncommon, extremely high magnesium levels can cause hypermagnesemia – an overabundance of magnesium in the bloodstream.
Symptoms of hypermagnesemia include lethargy, weakened muscles, and breathing difficulties.
In extreme cases, taking very large doses (exceeding 5,000 mg/day) of products like laxatives or antacids containing magnesium can lead to toxicity.
This may cause irregular heartbeats, lowered blood pressure, mental confusion, impaired breathing, and in the most severe instances, can be fatal.
Individuals with renal impairments are at a higher risk of accumulating toxic levels of magnesium because their compromised kidneys cannot efficiently excrete the excess.
It’s essential to be cautious when taking magnesium supplements alongside other medications that may either reduce its absorption or affect the efficacy of other drugs.
Careful label examination is crucial, as multivitamins, antacids, and laxatives often contain hidden sources of magnesium.
Consulting with knowledgeable pharmacists can provide accurate information and guidance on usage.
Additionally, while adding supplements to your diet is generally considered standard practice, it’s important to monitor recommended allowances and watch for signs of adverse reactions.
Protective measures are even more critical for those with existing health conditions or those on specific medication regimens.
After addressing these precautions, we can now explore the best food sources rich in magnesium to naturally boost your nutrient levels.
Best Dietary Sources of Magnesium
Ensuring adequate magnesium intake is best achieved through consuming it as part of the diet.
A wide range of foods, including some that are fortified, such as certain breakfast cereals, contain this essential mineral.
Rich sources include green leafy vegetables like spinach and kale. These foods are excellent for increasing one’s magnesium levels.
Seeds, nuts, and whole grains offer a bounty of magnesium-rich choices to seamlessly fit into any well-rounded eating plan.
Legumes also serve as wonderful options for obtaining more magnesium in your diet.
A single cup of cooked black beans contributes 120 mg, while half a cup of shelled edamame yields 50 mg.
Dairy products along with meats provide doses of this nutrient too just like chocolate and coffee do—offering diverse ways to accommodate distinct dietary needs or tastes—for instance snacking on almonds provides you with an impressive 76 mg per ounce whereas cashews come in slightly higher at 83 mg per ounce.
Foods such as extremely versatile tofu or creamy avocados can be considerable contributors to your daily dose.
- Consuming half a cup provides approximately 37 mg of magnesium.
- Avocados are nutritional powerhouses, making them ideal for various dishes. Whether blended into smoothies, spread on toast, added to salads and sandwiches, or enjoyed straight from the skin, they are a delicious way to boost your magnesium intake.
- Quinoa—a powerhouse grain—one prepared serving clocks around 118 mgs.
By integrating these items across meals increases the chances of meeting recommended thresholds foregoing tablets capsules altogether.
In summary, leveraging the power of plants across different food groups, notably green vegetables, a variety of seeds, and different types of nuts, can be sufficient to meet the magnesium needs of most people.
By thoughtfully planning your meals to include these magnesium-rich foods, you can maintain your overall well-being through diet alone.
Finally, we turn our lens toward interactions between type including its derivative citrate concurrently administered alongside other medicines drawing attention importance cautious approach mitigate risk experiencing adverse effects related compound interaction mechanisms.
Interactions Between Magnesium and Medications
The interaction of magnesium with different medications can influence how well these medications work.
For example, when combined with specific antibiotics, including tetracyclines and those belonging to the quinolone family, magnesium may impede their complete absorption.
It is advisable to consume magnesium supplements either at least two hours before or between four and six hours after taking such antibiotics to circumvent any potential negative interactions.
Magnesium has been found to interact with various drugs like:
- Antibiotics in the aminoglycoside category, for instance amikacin and gentamicin.
- Fluoroquinolone antibiotics like ciprofloxacin and tetracycline derivatives such as demeclocycline and minocycline.
- Hypertension medicines categorized under calcium channel blockers which encompass nifedipine along with verapamil.
Consulting healthcare professionals regarding correct dosage timing is essential in preventing drug interference.
Interactions are also seen between bisphosphonates (osteoporosis treatments) and magnesium—timing intake properly mitigates diminished drug efficacy.
Products containing magnesium could potentially interfere with cellulose sodium phosphate use or impact digoxin’s action.
Those prescribed thyroid hormones such as levothyroxine should get guidance from pharmacists on how best to schedule their intake of magnesium supplements so it doesn’t affect medication effectiveness.
While there are significant health benefits tied to using magnesium supplements—including managing blood pressure—it’s important not only to be aware but also vigilant about its possible interactions with other medicines one might be consuming.
Seeking advice from medical providers ensures safe utilization of these nutritional aids alongside prescribed treatment regimens without compromising efficiency.
Moving forward, we will address special considerations needed when certain individuals—such as pregnant women or those suffering from cardiovascular disease—decide whether they should take up supplementation that includes elements like Magnesium within their regimen.
Special Considerations for Different Groups
Diverse populations require tailored amounts of magnesium, and some are more vulnerable to potential supplementation risks.
For pregnant women, a daily dose of 350-360 milligrams is suggested to prevent complications related to pregnancy such as fetal growth restriction stemming from high blood pressure—making sufficient magnesium consumption critical for mothers-to-be.
Ensuring children receive an adequate supply of magnesium is vital for their growth and development.
While it is generally safe when taken orally in appropriate dosages, consulting with a pediatrician can help ensure that children’s dietary needs are met and that supplements are used correctly if needed.
Individuals with kidney disease must be especially cautious when using magnesium supplements, as their bodies might struggle to eliminate excess amounts, potentially leading to harmful accumulation and toxicity.
Similarly, those dealing with chronic diarrhea, celiac disease, or diabetes may experience increased magnesium loss, necessitating careful monitoring and possible supplementation.
Specific demographics including expectant mothers, growing children, and persons managing particular health issues have unique needs regarding their intake levels—and thus should seek personalized advice on incorporating supplemental sources safely into their regimen.
Summary
Magnesium is crucial for numerous bodily functions, including enzyme activity, blood sugar regulation, and blood pressure control.
While deficiency is uncommon in the general population, it can occur in those with chronic health conditions or poor diets.
Magnesium supplements may benefit these at-risk individuals by reducing blood pressure, preventing migraines, and supporting healthy pregnancies.
Healthy adults without deficiencies may not need additional supplementation. It’s essential to consult a healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen.
While generally safe within recommended limits, excessive magnesium intake can lead to side effects or interact with certain medications.
The most effective way to ensure adequate magnesium intake is through a balanced diet rich in leafy greens, seeds, nuts, whole grains, and legumes.
However, for those considering supplementation, a full-spectrum daily magnesium supplement may offer comprehensive support for various bodily functions.
Consider exploring a full-spectrum magnesium supplement option if you and your healthcare provider determine that magnesium supplementation is right for you.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the signs of magnesium deficiency?
Should you be suffering from fatigue, muscle cramps, nausea, or an irregular heartbeat, this might indicate that your body is low in magnesium. These symptoms typically manifest when the magnesium levels have dropped significantly.
It’s important to monitor these symptoms and think about seeking medical advice for a more comprehensive assessment.
How much magnesium should I take daily?
It’s advisable to consume approximately 350-400 mg of magnesium every day. It is crucial to seek tailored recommendations from a healthcare professional.
Can I get enough magnesium from my diet?
Yes, a balanced diet including green leafy vegetables, seeds, nuts, whole grains, and legumes can provide enough magnesium for most people.
Are there any risks associated with magnesium supplementation?
Indeed, taking magnesium supplements can lead to potential side effects such as gastrointestinal discomfort and, in extreme situations, magnesium toxicity.
It is essential to approach magnesium supplementation with care, particularly for individuals who suffer from kidney issues.
Can magnesium interact with medications?
Certainly, magnesium has the potential to influence the absorption and potency of a range of drugs. It is crucial to discuss possible interactions with your healthcare provider.
Magnesium for Sleep and Anxiety: Benefits, Dosage, and EffectsStruggling with sleepless nights and constant worry? Magnesium for sleep and anxiety might be the solution you’ve been searching for—this essential mineral plays a crucial role in calming your nervous system and promoting restful sleep.
Imagine falling asleep easily and waking up refreshed, free from anxious thoughts. Magnesium supplementation could make this a reality. With its ability to regulate neurotransmitters and relax muscles, magnesium offers a natural way to improve sleep quality and reduce anxiety symptoms.
Curious about how magnesium could transform your rest and overall well-being? This guide explores the benefits, dosages, and effects of magnesium for sleep and anxiety, helping you take the first step towards better nights and calmer days.
Key Takeaways
- Magnesium is essential for nerve and muscle function, bone development, blood sugar control, and regulating the nervous system, which helps with relaxation and sleep.
- Different forms of magnesium supplements, like magnesium glycinate, citrate, and oxide, offer unique benefits, especially for improving sleep quality and reducing anxiety.
- Magnesium can help treat various sleep disorders such as insomnia and restless leg syndrome.
- Full-spectrum magnesium supplements combine multiple forms of magnesium and co-factors, potentially offering a range of benefits for sleep, anxiety, and overall health.
- Adults should aim for a daily magnesium intake of 310-420 mg, but excessive intake can lead to potential side effects like nausea, vomiting, and irregular heartbeat, so it’s important to consult a healthcare professional before supplementing.
Understanding the Role of Magnesium

Magnesium is crucial for a myriad of vital bodily functions. It plays an essential role in various key areas including:
- Proper functioning of nerves and muscles.
- Bone strength.
- Regulating blood sugar levels.
- Maintaining regular heart rhythm.
Beyond these physical roles, magnesium contributes to mental well-being by soothing the nervous system and contributing to muscle relaxation—two important factors that can enhance sleep quality.
In our everyday experience, adequate magnesium levels can lead to enhanced tranquility, reduced instances of muscle cramps, and better emotional balance.
This stems from its ability to modulate neurotransmitters and stimulate GABA receptors that help control the nervous system’s activity and promote calmness.
Hence, a deficit in magnesium may cause feelings of anxiety or disturb restful sleep due to closeness with nerve operation principles it holds.
Magnesium can also help treat sleep disorders such as insomnia and restless leg syndrome.
Types of Magnesium Supplements
Like other dietary supplements, a magnesium supplement is not universally applicable to everyone’s needs.
Different forms offer distinct advantages, especially when it comes to promoting sleep and alleviating anxiety.
It’s important to consider the various prevalent kinds of magnesium supplements such as magnesium glycinate, magnesium chloride, magnesium citrate, and magnesium oxide. Each possesses specific characteristics beneficial for the health concerns they address.
Magnesium Glycinate
Magnesium glycinate is comprised of magnesium and glycine, an amino acid lauded for its superior absorption capabilities and soothing effects. This variant of magnesium is especially adept at increasing the body’s magnesium levels.
Individuals frequently utilize magnesium glycinate to calm both mind and body, which can potentially diminish stress and anxiety.
This compound exerts a tranquillizing influence on the nervous system that may assist people in falling asleep faster while promoting deeper sleep cycles.
Although comprehensive scientific research directly associating magnesium glycinate with enhanced sleep is sparse, numerous personal accounts indicate it might significantly benefit those dealing with insomnia.
Magnesium Citrate
Magnesium citrate, often recognized for its effectiveness as a laxative in addressing constipation, also offers advantages that go beyond just aiding digestion.
Its superior bioavailability makes it a form of magnesium readily assimilated by the body when compared to alternative forms.
Not only is magnesium citrate sought after for its bowel-regulating properties, but individuals also turn to it as an aid to enhance sleep quality because of its efficient uptake.
This specific type may prove especially advantageous for those suffering from a magnesium deficiency and experiencing disrupted sleep patterns, promoting the attainment of tranquil and restful slumber.
Magnesium Oxide
Despite its high magnesium concentration per dose, magnesium oxide might not be as readily absorbed compared to other variants.
It can still serve effectively in mitigating the manifestations of a magnesium deficiency. It is commonly utilized for bolstering nerve and muscle function, playing a role that may enhance sleep quality.
This particular form of magnesium has been recognized for its capacity to diminish anxiety and promote mental well-being.
Although it may not suit every individual perfectly, due to its potent quantity of magnesium, many consider it an efficient alternative when aiming to increase their intake of this essential mineral.
Full-Spectrum Magnesium Solutions: Magnesium 7
When considering magnesium supplementation for sleep and anxiety, a full-spectrum option like Magnesium 7 offers a comprehensive approach. This supplement combines seven forms of elemental magnesium, each with unique benefits:
- Magnesium Chelate for muscle recovery.
- Magnesium Glycinate for sleep, anxiety, and brain health.
- Magnesium Aspartate for mood support.
- Magnesium Malate for brain and nervous system function.
- Magnesium Orotate for heart health and exercise performance.
- Magnesium Taurate for relaxation and blood pressure regulation.
- Magnesium Citrate for cardiovascular and intestinal health.
Magnesium 7 also includes co-factors like Vitamin B6, which has been shown to enhance stress reduction when combined with magnesium, and Manganese Citrate for bone strength.
This full-spectrum approach may provide a range of benefits, including:
- Reduced stress and anxiety levels.
- Improved sleep quality.
- Support for heart health and bone strength.
- Enhanced nutrient absorption and energy production.
- Healthy cellular and nerve function.
- Muscle mass maintenance and sore muscle relief.
For those seeking a comprehensive magnesium supplement that addresses multiple aspects of health, including sleep and anxiety, Magnesium 7 presents an interesting option.
Consider discussing this supplement with your healthcare provider to determine if it’s right for your individual needs and health goals.
How Magnesium Helps With Sleep
Magnesium supplementation serves an essential role in promoting better sleep by increasing the activity of GABA and managing melatonin levels within the brain.
By doing so, it helps soothe the mind, allowing for easier initiation of sleep as well as improved maintenance of uninterrupted rest throughout the night.
Additionally, magnesium can promote a good night’s sleep by regulating melatonin and increasing GABA levels.
Known to assist with muscle relaxation through its effect on activating the parasympathetic nervous system, magnesium—which is often referred to when discussing magnesium for sleep—prepares your body optimally for slumber.
This enables you to not only fall asleep more smoothly, but also experience a deeper and more rejuvenating sleep cycle.
Research supports that using magnesium supplements can notably enhance both how long one sleeps and the quality of that sleep. It stands out as a potent solution for those contending with insomnia or other types of sleep disturbances.
Reducing Insomnia Symptoms
Magnesium plays a crucial role in enhancing sleep by alleviating symptoms of insomnia. This is accomplished through several means:
- Elevating levels of GABA within the brain, which promotes a soothing impact on the central nervous system.
- Facilitating the process to both fall asleep and remain asleep consistently.
- Ensuring that one’s sleep throughout the night is more tranquil and restorative.
Magnesium can also help treat sleep disorders such as insomnia.
Alleviating Restless Leg Syndrome
Magnesium plays a pivotal role in combating the symptoms of restless leg syndrome (RLS), which often impedes one’s ability to experience restful sleep.
This crucial mineral aids in muscle relaxation and diminishes discomfort by maintaining optimal muscle function, thus potentially easing the muscular tension and cramping that RLS frequently causes.
Those suffering from RLS who have diminished magnesium levels may encounter more pronounced symptoms.
As such, supplementing with magnesium presents itself as an effective strategy for mitigating these issues.
By alleviating muscular pain and stiffness associated with RLS, enhancing magnesium intake is instrumental in improving sleep quality for affected individuals.
How Magnesium Helps With Anxiety
Magnesium supplementation is not only beneficial for sleep enhancement, but it also has a crucial impact on anxiety management.
The mineral modulates brain neurotransmitters that calm the body, thereby exerting significant influence on mood stabilization and stress response mechanisms.
Stress can escalate when magnesium levels are insufficient.
Conversely, heightened states of physical or emotional strain may drain the body’s reserves of magnesium.
It is therefore vital to sustain proper levels of this nutrient to effectively manage anxiety as well as promote general mental wellbeing.
Evidence from research indicates that enhancing one’s intake of magnesium can alleviate symptoms associated with depression and diminish experiences of anxiety, making it an important component in supporting mental health care strategies.
Balancing Neurotransmitters
Magnesium plays a vital role in the regulation of mood by maintaining the equilibrium of neurotransmitters and neuroreceptors within the brain.
Its consumption is linked to diminished systemic inflammation, which is considered a contributing risk factor for various psychological disorders.
Enhancing Cognitive Function
To equilibrate neurotransmitters, magnesium boosts cognitive abilities by influencing different neural processes.
It acts as a strong inhibitor of the NMDA receptor complex, pivotal in sustaining effective neuron communication and brain function.
The advantages of magnesium for mental sharpness and emotional health are many.
- Magnesium augments the levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which is linked with preserving cognitive wellness.
- It facilitates enhanced concentration and mental focus.
- The mineral assists in alleviating feelings of anxiety.
Given these impacts, magnesium stands out as an essential component for nurturing both cognitive prowess and emotional stability.
Recommended Dosage of Magnesium
Ensuring an appropriate dosage is key when it comes to magnesium supplementation.
Adults should consume a daily amount that ranges from 310 mg to 420 mg, depending on their gender and age. Here’s what the daily intake recommendations look like:
- At least 310 mg per day for women.
- Up to 420 mg each day for men.
- An increase between 350 and 360 mg every day during pregnancy is advised in order to support both the mother and her growing baby.
Before you start taking magnesium supplements, it’s imperative to seek advice from a medical expert, especially if considering higher dosages.
Safe, magnesium supplements can trigger adverse effects if one consumes over 350 milligrams per day.
Daily Dietary Intake
Grasping the recommended amount of magnesium for daily dietary intake is essential to ensure sufficient nutrient levels and bolster general well-being.
A common question arises: “How much magnesium should I consume daily?” The suggested daily consumption for adult women lies in the range of 310 to 320 milligrams, which is crucial to keep track of.
Supplement Dosage Guidelines
It’s been observed that older adults experiencing insomnia and consuming between 320-729 mg of magnesium daily tend to fall asleep faster than those in a placebo group.
It is critical to adhere strictly to supplement dosage recommendations because ingesting over 350 milligrams can lead to adverse reactions.
Potential Side Effects of Magnesium
It’s important to be aware of the potential adverse effects associated with magnesium supplements, despite their numerous health benefits.
Excessive consumption beyond the recommended daily amount can result in magnesium toxicity, manifesting as symptoms that include nausea, vomiting, muscle cramps, diarrhea and irregular heartbeat.
Extreme cases of too much magnesium intake may lead to serious complications such as an irregular heartbeat, decreased blood pressure levels leading up to confusion state conditions slowed breathing rates possibly culminating in a coma or even fatality.
For those aiming at prevention of gastrointestinal discomfort, it is suggested that one takes these supplemental elements alongside food consumption periods.
Individuals with kidney dysfunctions should exercise additional caution, as they are more susceptible to accumulating hazardous levels of magnesium in their system.
Supplementing with this mineral can also slow down the coagulation process, posing a risk of bleeding or bruising for individuals with clotting disorders.
Therefore, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider before starting supplementation.
Foods Rich in Magnesium
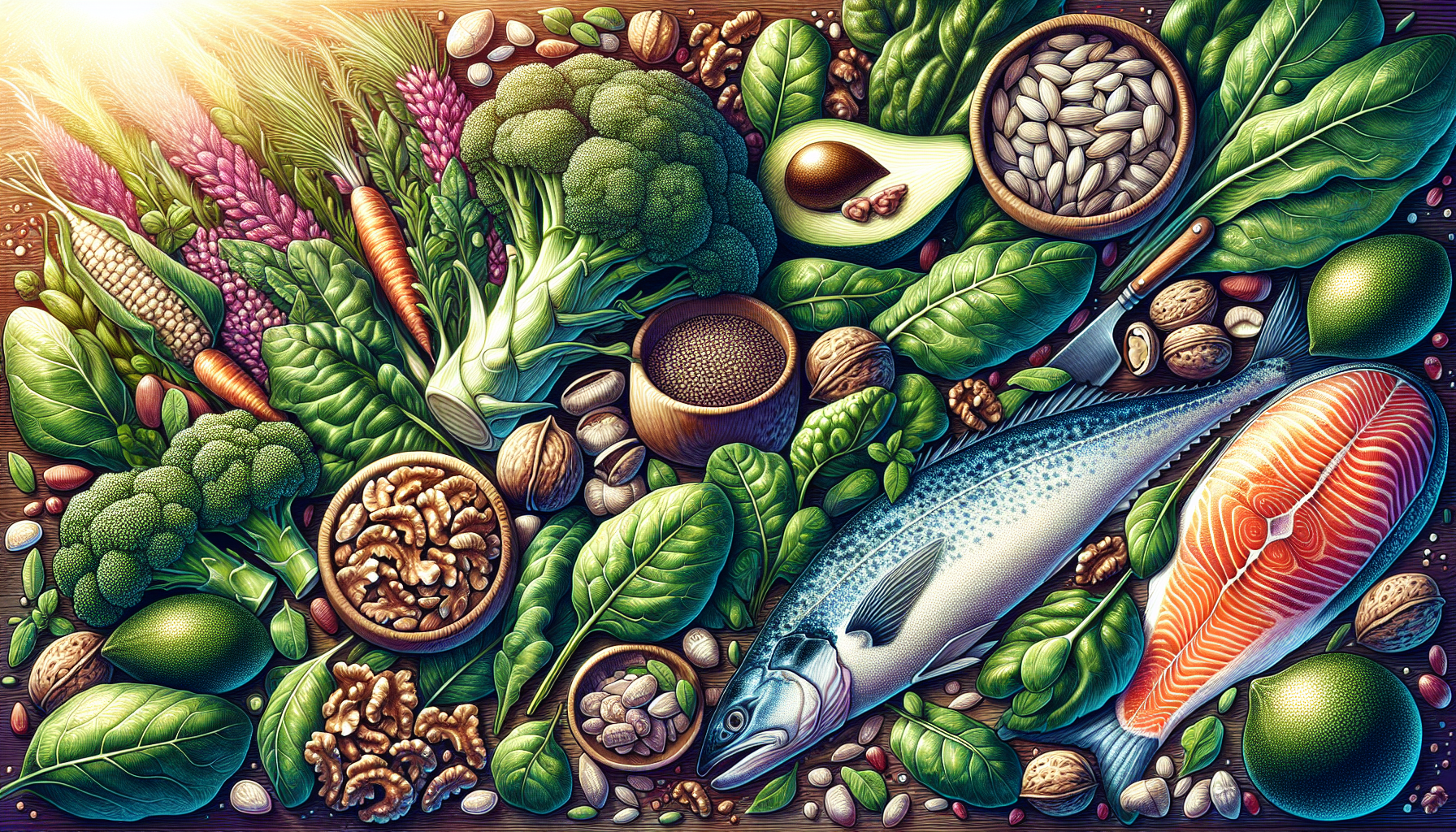

Adding foods to your diet that are high in magnesium can naturally enhance your body’s magnesium levels. Notable sources of this vital mineral include:
- Pumpkin seeds, which contain 150 mg of magnesium for every ounce.
- Chia seeds with a contribution of 111 mg of magnesium per ounce.
- Dark leafy vegetables like cooked spinach offer about 78 mg per half-cup.
- Cooked Swiss chard provides roughly 75 mg per half-cup.
Nuts such as almonds, providing around 80 mg per ounce, and cashews at about 72 mg per ounce, along with fish varieties like salmon, are rich in magnesium, too.
By incorporating these nutrient-dense options into what you eat regularly, you could support better sleep quality and play a role in alleviating anxiety without resorting to supplements.
Tips for Taking Magnesium Supplements
When consuming magnesium supplements, it’s crucial to pay attention to both the timing of intake and the precise amount taken.
If you’re using extended-release tablets of magnesium, they must be consumed intact. Refrain from chewing or dissolving them in your mouth.
If you have certain other types of magnesium tablets that are designed to be broken or crushed, you may combine them with a soft food substance—though always seek advice from a healthcare provider before doing so.
For those who opt for powdered forms of magnesium supplements, ensure that the powder is fully dissolved in water and stirred thoroughly prior to drinking it.
Pairing your regimen with Vitamin B12 might enhance the absorption rates of magnesium, which can amplify its effectiveness.
Who Should Consider Magnesium Supplementation?
Magnesium supplementation can be advantageous for a wide range of individuals. It is estimated that half the population does not consume sufficient magnesium through their diets alone.
Those suffering from type 2 diabetes might require magnesium supplements because they tend to lose more of it via urine.
People with health issues that hinder the absorption of magnesium may find supplementation beneficial.
Individuals who are dealing with persistent tiredness, stress, or anxiety may discover that taking magnesium supplements is especially useful.
Due to biochemical individuality—where certain bodies demand more magnesium than what dietary intake supplies—supplementation could be considered necessary by some.
Summary
Magnesium is essential for health, offering benefits for sleep quality and anxiety reduction. Various supplement forms are available, each with unique advantages. Ensuring adequate intake through diet or supplementation is key to maximizing magnesium’s benefits.
Full-spectrum options like Magnesium 7, which combine multiple magnesium forms and co-factors, offer a comprehensive approach. However, always consult a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen to determine the best option for your specific needs.
By making informed choices about magnesium supplementation, you can take proactive steps towards better sleep, reduced anxiety, and improved overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main benefits of magnesium for sleep?
Incorporating magnesium into your daily regimen can enhance sleep quality by aiding GABA activity, managing melatonin production, and soothing muscle tension, which all contribute to achieving better sleep.
How does magnesium help with anxiety?
By regulating brain chemical messengers, stabilizing neurotransmitter balance, and diminishing stress levels, magnesium aids in managing anxiety.
What is the recommended daily intake of magnesium for adults?
It is advised that adult men should consume up to 420 milligrams of magnesium daily. In contrast, the suggested intake for adult women ranges from 310 to 320 milligrams.
To maintain a well-rounded diet, it’s important to fulfill this nutritional guideline.
What are some magnesium-rich foods?
To boost your magnesium intake, consider adding foods such as pumpkin seeds, spinach, almonds, and salmon to your meals.
Each of these items is a plentiful source of this essential mineral.
What are the potential side effects of taking too much magnesium?
Exceeding the recommended dosage of magnesium can result in side effects such as vomiting, nausea, diarrhea, cramping, and an abnormal heartbeat. It is crucial to adhere to the recommended amounts to prevent these adverse reactions.
Magnesium for Depression: The Science Behind Its EffectivenessAre you battling depression and seeking a natural solution? Magnesium for depression is emerging as a promising option, offering hope where traditional treatments may fall short.
This essential mineral, often overlooked in mental health discussions, plays a crucial role in brain chemistry.
Recent studies suggest that magnesium could significantly reduce depressive symptoms, potentially offering an affordable, fast-acting, and well-tolerated approach to managing mood disorders.
In this guide, you’ll discover how magnesium impacts brain function, explore the latest research on its effectiveness for depression, and learn practical ways to incorporate it into your mental health regimen.
Whether you’re looking for an alternative to conventional treatments or aiming to enhance your current approach, understanding the potential of magnesium for depression could be your next step towards improved mental well-being.
Key Takeaways
- Magnesium plays a crucial role in mental health by interacting with key brain receptors and enzymes, helping to regulate mood and potentially alleviate depression.
- Research, including randomized controlled trials, indicates that magnesium supplementation can significantly reduce depression symptoms, often showing quicker results compared to traditional antidepressants.
- Different forms of magnesium supplements vary in their bioavailability, with magnesium citrate and magnesium chloride being more effective due to their higher absorption rates, making them better choices for addressing magnesium deficiency and depressive symptoms.
- Full-spectrum magnesium supplements combine multiple forms of magnesium, potentially offering broader health benefits including mood support.
Understanding the Role of Magnesium in Mental Health
Magnesium is integral to our mental well-being, acting as a protective shield for our brain’s delicate balance.
This essential mineral serves as a co-factor in over 350 enzymes in the human body, many of which are vital for proper brain function.
Its importance in mood regulation cannot be overstated, as it helps to balance and control various neurotransmitters that influence our emotional state.
One of the key ways magnesium impacts our mental health is through its interaction with the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor.
By blocking the ion channel of this receptor, magnesium prevents its excessive activation and protects nerve cells from an influx of calcium.
This modulation of neurotransmission in the central nervous system supports psychiatric and neurological stability.
Additionally, magnesium’s role in modulating the central nervous system and its impact on systemic inflammation, sleep disturbances, and mood disorders can also be beneficial for postpartum depression.
A deeper look into the science behind magnesium’s effects on depression reveals how the mineral’s unique properties can potentially improve mental health outcomes.
The science behind magnesium and depression
The link between magnesium and depression stems from the mineral’s core role in brain function.
As we’ve mentioned, magnesium acts as a co-factor in more than 350 enzymes in humans, many of which are crucial for maintaining optimal brain health.
This extensive involvement in brain chemistry allows magnesium to influence mood regulation by balancing various chemical compounds in the brain.
A notable aspect of magnesium’s influence on depression is its interaction with the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor.
Magnesium is a potent antagonist of this receptor complex, which plays a significant role in regulating mood and cognitive function.
By inhibiting excessive NMDA receptor activity, magnesium helps maintain a healthy balance of neurotransmitters in the brain, potentially alleviating symptoms of depression.
Furthermore, magnesium has been shown to affect other key players in the brain’s mood regulation system.
For instance, it inhibits glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK-3), an enzyme that has been implicated in mood disorders.
Interestingly, this inhibition is similar to the action of several antidepressant medications, suggesting that magnesium may work through similar pathways to improve mood.
Several studies have conducted randomized clinical trials to assess the impact of magnesium supplements on depression, highlighting significant findings that support its effectiveness in reducing depression symptoms.
For example, a randomized clinical trial by Tarleton et al. demonstrated that magnesium supplementation could significantly alleviate depressive symptoms.
Further supporting the link between this mineral and mood disorders, research has revealed that body magnesium levels can fluctuate during depressive episodes.
Brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and magnesium
Another fascinating aspect of magnesium’s role in mental health is its relationship with brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF).
BDNF is a protein that plays a crucial role in the growth, maintenance, and survival of neurons in the brain. It’s often referred to as “fertilizer for the brain” due to its importance in cognitive function and mental health.
Interestingly, magnesium levels are closely linked to the expression of BDNF, highlighting yet another way this mineral contributes to our mental well-being.
Studies have shown that supplementing with magnesium can enhance the expression of BDNF in the brain, especially in the prefrontal cortex.
This effect is similar to that observed with ketamine, a drug that has gained attention for its rapid antidepressant effects.
The increase in BDNF expression is thought to contribute significantly to the antidepressant effects of both magnesium and ketamine.
By promoting the growth and plasticity of neurons, increased BDNF levels may help the brain adapt and recover from the neural changes associated with depression, potentially leading to improved mood and cognitive function.
Research on Magnesium Supplementation for Depression
With the potential link between magnesium and depression becoming more apparent, researchers have shifted their focus to explore the effects of magnesium supplementation on depressive symptoms.
The results have been promising, with numerous studies showing that magnesium supplementation can significantly reduce and improve depression scores.
This effect seems to be particularly pronounced when magnesium is used in combination with antidepressants, suggesting a potential synergistic effect that could enhance treatment outcomes for those struggling with depression.
Specific studies have conducted randomized controlled clinical trials to assess the impact of magnesium supplements on depression, including findings that highlight the potential benefits of adding magnesium to existing antidepressant treatments.
One compelling feature of magnesium as a potential depression treatment is its affordability, rapid action, and general tolerability.
These characteristics make it an attractive option for those seeking alternative or complementary treatments for depression.
Moreover, some researchers suggest that magnesium treatment in clinical trials could be as effective as, or even more effective than, traditional antidepressant drugs.
This potential has led to increased interest in magnesium as a treatment option, particularly for individuals who have not responded well to conventional antidepressant therapies.
Randomized controlled trials
Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have been instrumental in confirming the efficacy of magnesium supplementation for depression.
These rigorous studies offer the most reliable evidence in medical research, enabling more conclusive insights about the effects of magnesium on depressive symptoms.
Several RCTs have investigated the impact of magnesium supplements on patients with major depressive disorders, yielding valuable insights into this potential treatment approach.
One notable study examined the effects of magnesium chloride supplementation on depression scores over a six-week period.
The results were striking: participants who received magnesium chloride reported a net improvement of -6.0 points in their depression scores.
This significant reduction in symptoms suggests that magnesium supplementation could have a meaningful impact on the lives of those struggling with depression.
Another study focused on the effects of magnesium supplementation over a longer period. Researchers found that:
- The mean Beck scores (a widely used measure of depression severity) of patients in the magnesium intervention group were lower compared to the control group after just four weeks of treatment.
- This rapid improvement is particularly encouraging, as many traditional antidepressants can take several weeks to show noticeable effects.
- The study also noted that these improvements continued throughout the intervention period, with mean Beck scores decreasing further in the magnesium group compared to the placebo group by the end of the study.
Systematic reviews and meta-analyses
While individual studies offer important insights, systematic reviews, and meta-analyses broaden the perspective by amalgamating data from multiple trials.
A comprehensive meta-analysis of randomized controlled trialsinvestigating magnesium supplementation for depression has revealed some exciting findings.
The analysis, which adhered to the PRISMA protocol for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses, initially identified over 3,000 publications related to the topic, including those on selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors.
After rigorous screening, seven eligible randomized controlled trials were included in the final analysis. The results were compelling:
- The meta-analysis found that magnesium supplementation caused a significant drop in depression scores compared to placebo.
- Interestingly, a subgroup analysis suggested that lower doses of magnesium supplements (250 mg/day or less) may have a stronger effect on reducing depression scores than higher doses.
- This finding highlights the importance of proper dosing in magnesium supplementation and suggests that more isn’t always better when it comes to this mineral’s effects on mental health.
Types of Magnesium Supplements
When considering magnesium supplementation for depression, it’s important to know that not all forms of the mineral are alike.
There are several types of magnesium supplements available on the market, each with its own unique properties and potential benefits. The most common forms include:
- Magnesium oxide.
- Magnesium citrate.
- Magnesium chloride.
- Magnesium sulfate.
Understanding the differences between these supplements is important for anyone considering adding magnesium supplementation to their mental health regimen.
The key factor that distinguishes these different forms of magnesium is their bioavailability – that is, how easily they are absorbed and utilized by the body.
This factor can significantly influence the effectiveness of the supplement in addressing magnesium deficiency and potentially improving depressive symptoms.
For instance, magnesium oxide, while commonly used, has a lower bioavailability compared to other forms.
On the other hand, magnesium citrate is known for its superior absorption rate, making it a popular choice for those seeking to increase their magnesium levels effectively.
Magnesium chloride vs. magnesium sulfate
When comparing different forms of magnesium supplements, magnesium chloride and magnesium sulfate are two options that often come up in discussions about mental health.
Both have their unique properties and potential benefits, but magnesium chloride tends to stand out when it comes to oral supplementation for depression.
Magnesium chloride is often praised for its ability to replenish magnesium levels quickly due to its excellent absorption properties.
This rapid absorption makes it particularly beneficial for treating depression, as it can effectively raise magnesium levels in the body, potentially leading to faster symptom relief.
Moreover, magnesium chloride is considered superior for oral supplementation due to its high solubility, which contributes to its impressive absorption rate.
These characteristics make magnesium chloride a popular choice among those looking to address magnesium deficiency and its potential impact on mental health.
Magnesium oxide and magnesium citrate
When it comes to magnesium supplements, two forms that are frequently compared are magnesium oxide and magnesium citrate.
While both can increase magnesium levels in the body, they differ significantly in their absorption rates and overall effectiveness.
Magnesium citrate is often the preferred choice for those seeking to boost their magnesium levels due to its higher bioavailability.
This means that a larger proportion of the magnesium in this form is absorbed by the body, making it more effective at increasing overall magnesium levels.
On the other hand, magnesium oxide has one of the lowest bioavailability rates among magnesium supplements.
This lower absorption rate means that while magnesium oxide supplements may contain a high percentage of elemental magnesium, less of it actually makes its way into the body’s systems where it can have an impact on mental health.
As a result, when comparing these two supplements for their potential effects on depression, magnesium citrate generally comes out on top due to its superior ability to raise magnesium levels in the body effectively.
Full-Spectrum Magnesium Supplementation: A Comprehensive Approach
While single-form magnesium supplements can be beneficial, full-spectrum magnesium supplements offer a more comprehensive approach to addressing various aspects of health, including mental well-being.
These supplements typically combine multiple forms of elemental magnesium, each with its own unique benefits:
- Magnesium Chelate: Supports muscle recovery.
- Magnesium Glycinate: Promotes sleep, anxiety relief, and brain health.
- Magnesium Aspartate: May help with mood, anxiety, and depression.
- Magnesium Malate: Supports brain and nervous system function.
- Magnesium Orotate: Beneficial for heart health and exercise performance.
- Magnesium Taurate: May help with blood pressure and relaxation.
- Magnesium Citrate: Supports cardiovascular and intestinal health.
Many full-spectrum formulations also include co-factors that can enhance magnesium’s effectiveness:
- Vitamin B6: May improve stress reduction when combined with magnesium.
- Manganese: Supports bone strength.
Potential Benefits of a full-spectrum magnesium supplementation also include:
- Stress and anxiety reduction.
- Improved sleep quality.
- Heart and bone health support.
- Enhanced nutrient absorption and energy production.
- Healthy cellular and nerve function.
- Muscle mass maintenance and post-exercise recovery.
While these potential benefits are promising, it’s important to note that individual results may vary. As with any supplement regimen, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting.
If you’re considering a magnesium supplement to support your mental health, a full-spectrum formulation may offer a well-rounded approach.
Look for a high-quality supplement that combines various forms of magnesium with supporting nutrients for optimal results.
Dosage and Safety Considerations

When considering magnesium supplementation for depression, it’s important to understand the appropriate dosage and be aware of potential safety concerns.
The recommended daily intake of magnesium varies depending on age and gender.
The recommended daily amount of magnesium for adult men ranges between 400 and 420 mg.
For adult women, the range is between 310 and 320 mg. It’s important to note that these recommendations cover total magnesium intake from both dietary sources and supplements.
While magnesium supplementation can be beneficial for many people, it’s not without potential side effects, especially when taken in very high doses.
Some individuals may experience abdominal pain, diarrhea, or nausea if they consume excessive amounts of magnesium.
In rare cases, very high intakes could lead to heart problems.
However, it’s worth noting that in studies on magnesium supplementation for depression, no explicit side effects were observed.
This suggests that when taken within recommended doses, magnesium supplements are generally well-tolerated by most individuals.
Recommended dietary magnesium intake
Being aware of the recommended dietary intake of magnesium is key to maintaining optimal mental health and potentially easing depressive symptoms.
For adult men, the daily recommended magnesium intake is between 400 to 420 milligrams, while for adult women, it’s slightly lower at 310 to 320 milligrams per day.
These recommendations are based on extensive research and are designed to ensure that most individuals meet their basic magnesium needs through diet and supplementation if necessary.
It’s important to note that certain life stages may require adjustments to magnesium intake.
For instance, pregnant women over 18 years of age are advised to increase their magnesium intake to 350–360 mg per day to support both maternal and fetal health.
Additionally, some studies have shown potential benefits of higher magnesium intake for specific groups.
A review of three studies among older adults found that supplementing with 320 to 720 mg of magnesium daily for up to 8 weeks yielded improvements in sleep quality, which can indirectly support mental health.
This highlights the potential benefits of magnesium supplementation beyond just meeting basic nutritional needs, especially when it comes to mental health and well-being.
Potential side effects and interactions
Although magnesium supplementation can be beneficial for many people, particularly those dealing with depression, it’s important to be cognizant of possible side effects and interactions.
One of the primary concerns with magnesium supplementation is the risk of toxicity if the recommended intake is exceeded.
This underscores the importance of adhering to recommended dosages and consulting with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
The symptoms of magnesium toxicity can be uncomfortable and may include nausea, abdominal cramping, and diarrhea.
These gastrointestinal symptoms are often the first signs that magnesium intake has exceeded the body’s ability to process it effectively.
It’s worth noting that these side effects typically occur only with excessive intake, and most people can safely take magnesium supplements within the recommended dosage range without experiencing adverse effects.
However, to ensure safety and maximize the potential benefits for mental health, it’s crucial to adhere to the recommended dosages of magnesium and to consult with a healthcare professional, especially if you’re taking other medications or have existing health conditions.
Practical Tips for Increasing Magnesium Intake

Boosting your magnesium intake isn’t synonymous with relying solely on supplements.
In fact, one of the most effective and natural ways to boost your magnesium levels is through dietary changes.
Incorporating more magnesium-rich foods into your daily meals can significantly contribute to meeting your recommended intake. Some examples of magnesium-rich foods include:
- Leafy greens.
- Nuts.
- Seeds.
- Whole grains.
- Beans.
By making conscious choices to include these foods in your diet, you can support your mental health while also enjoying a diverse and nutritious range of foods.
For those who struggle to meet their magnesium needs through diet alone, or for individuals with increased magnesium requirements, supplementation can be a beneficial option.
However, choosing the right supplement is crucial for maximizing the potential benefits. Factors such as bioavailability, form of magnesium, and individual health needs should all be considered when selecting a magnesium supplement.
In the following sections, we’ll explore both dietary sources of magnesium and tips for choosing the most suitable supplement to support your mental health journey.
Dietary sources of magnesium
Incorporating magnesium-rich foods into your diet is a delicious and natural way to boost your intake of this essential mineral.
Nature provides us with an abundance of magnesium sources, many of which can be easily integrated into our daily meals. Some of the best dietary sources of magnesium include:
- Nuts.
- Seeds.
- Leafy green vegetables.
- Beans.
- Dark chocolate.
Let’s explore some specific foods and their magnesium content to help you make informed choices about your diet.
Seeds are particularly rich in magnesium.
Pumpkin seeds, for instance, are a magnesium powerhouse, providing an impressive 168-156 milligrams of magnesium per ounce.
Chia seeds are another excellent option, offering 111 milligrams of magnesium per ounce.
Nuts are also a great source of magnesium, with almonds containing 80 milligrams per ounce and cashews providing 74 milligrams per ounce.
Leafy green vegetables are not only packed with various vitamins and minerals but are also rich in magnesium. Some examples include:
- Half a cup of boiled spinach contains 78 milligrams of magnesium.
- Legumes like black beans provide 60 milligrams of magnesium per half cup when cooked.
- Dark chocolate with 60-69% cocoa content contains about 50 milligrams of magnesium per ounce.
By incorporating a variety of these foods into your diet, you can significantly boost your magnesium intake and potentially support your mental health in a natural and enjoyable way.
Choosing the right supplement
While getting magnesium through diet is ideal, there are times when supplementation is necessary to meet your body’s needs, particularly when dealing with mental health issues like depression.
When choosing a magnesium supplement, it’s important to understand that not all forms are created equal.
The market offers various types of magnesium supplements, including:
- Magnesium chloride
- Magnesium sulfate
- Magnesium oxide
- Magnesium citrate
Each of these forms has different properties that affect how well they are absorbed and utilized by the body.
The absorption rate, or bioavailability, of a magnesium supplement is a crucial factor to consider. For instance, magnesium chloride and magnesium sulfate have different absorption rates, which can impact their effectiveness for specific health conditions, including depression.
Similarly, magnesium oxide and magnesium citrate vary in their bioavailability, which can influence their efficacy in treating depressive symptoms.
Generally, magnesium citrate and magnesium chloride are often recommended due to their higher absorption rates.
However, the best choice may vary depending on individual factors such as your specific health needs, any existing medications you’re taking, and your doctor’s recommendations.
It’s always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen, especially when it’s intended to support mental health.
Summary
Magnesium plays a vital role in mental health, particularly in managing depression.
Scientific evidence supports its potential to alleviate depressive symptoms through various mechanisms, including neurotransmitter regulation and BDNF production.
While dietary sources are beneficial, supplementation may be necessary for optimal results.
Full-spectrum magnesium supplements offer a comprehensive approach, combining different forms of magnesium to address various aspects of mental and physical health. These supplements may provide broader benefits compared to single-form options.
If you’re considering magnesium for depression management, consult with a healthcare professional about incorporating a high-quality, full-spectrum magnesium supplement into your routine.
This natural approach could be a valuable addition to your mental health strategy, potentially offering relief and improved well-being.
Take action today: Explore full-spectrum magnesium supplements and take a step towards better mental health.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take for magnesium supplements to start working for depression?
It may take around 2-4 weeks to see improvements in depression scores after starting magnesium supplementation, but consistency in taking the supplement and maintaining proper dosage is crucial for potential benefits.
Can magnesium supplements interact with antidepressant medications?
Yes, magnesium supplements can potentially interact with certain antidepressant medications, so it’s important to consult with your healthcare provider before taking them together to ensure safety and avoid potential interactions.
What’s the best form of magnesium supplement for depression?
The best form of magnesium supplement for depression can vary depending on individual factors.
Magnesium citrate and magnesium chloride are often recommended due to their higher absorption rates, but it’s best to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable form for your specific needs.
Are there any side effects of taking magnesium supplements for depression?
Yes, there can be some side effects of taking magnesium supplements for depression, such as diarrhea, nausea, or abdominal cramping, especially at higher doses.
If you experience any adverse effects, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider.
Can I get enough magnesium from my diet alone to help with depression?
In conclusion, while it’s possible to get magnesium from your diet, many people don’t get enough solely from food, so supplementation may be necessary for managing depression.
Always seek advice from a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
Magnesium Advantages: 9 Surprising Benefits For Your HealthFeeling tired, stressed, or plagued by headaches? The solution might be simpler than you think. The magnesium advantages could be the key to unlocking your overall health and well-being.
From supporting heart health to strengthening bones and improving sleep quality, magnesium plays a crucial role in hundreds of bodily functions. This essential mineral also helps manage stress, provides migraine relief, and enhances muscle performance.
Imagine waking up refreshed, tackling your day with energy, and experiencing fewer aches. With proper magnesium intake, this could be your reality.
Ready to harness the power of magnesium? Read on to explore how this mighty mineral can transform your health and discover simple ways to boost your intake.
Key Takeaways
- Magnesium supports various essential bodily functions, including heart health, by regulating blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and maintaining a regular heartbeat.
- For bone health, magnesium is vital for bone formation and density, working with calcium and vitamin D to prevent osteoporosis and maintain strong bones.
- Magnesium plays a key role in regulating blood sugar levels, improving insulin sensitivity, and potentially helping manage and prevent diabetes.
- Full-spectrum magnesium supplements combine multiple forms of magnesium, potentially offering a comprehensive range of health benefits in a single product.
- Consuming magnesium-rich foods is important for maintaining adequate magnesium levels and supporting overall health.
Heart Health

Magnesium holds a vital role in maintaining a healthy heart. This essential mineral is a true cardiovascular champion, working tirelessly behind the scenes to keep your heart beating strong and steady.
We will examine how magnesium supports heart health and the significance of maintaining adequate levels of this essential nutrient.
First and foremost, magnesium is a master regulator of blood pressure, including diastolic blood pressure.
High blood pressure is a significant risk factor for heart disease, but magnesium supplements can help lower those numbers, keeping your cardiovascular system in check.
It’s not just any form of magnesium that does the trick, though.
Magnesium taurate, in particular, has shown promise in lowering blood pressure and protecting the cardiovascular system.
This means that by maintaining adequate magnesium levels, you’re taking a proactive step in safeguarding your heart health.
However, the benefits of magnesium for heart health extend beyond blood pressure control. This mineral is also a key player in managing cholesterol levels, another critical factor in heart disease risk.
Magnesium helps regulate cholesterol, ensuring a healthy balance between LDL (the “bad” cholesterol) and HDL (the “good” cholesterol).
Studies have shown that magnesium supplements can improve multiple risk factors for heart disease, including LDL and HDL cholesterol, triglycerides, and systolic blood pressure levels.
This is especially true for individuals with a magnesium deficiency, highlighting the importance of maintaining optimal magnesium levels for heart health.
Another crucial aspect of magnesium’s role in heart health is its ability to support a regular heartbeat.
Magnesium helps the heart beat regularly, preventing arrhythmias and other cardiac irregularities. This rhythmic regulation is essential for overall heart function and can significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular events.
By ensuring your body has sufficient magnesium, you’re helping your heart maintain its natural, healthy rhythm.
The cumulative effect of magnesium’s various cardiovascular benefits is nothing short of impressive.
High intake of magnesium has been consistently linked to a lower risk of heart disease, stroke, and high blood pressure based on research findings. These findings demonstrate the potential health benefits of including magnesium in one’s diet.
This means that by prioritizing magnesium-rich foods in your diet or considering magnesium supplements, you’re taking a significant step towards reducing your risk of cardiovascular disease.
As with any health-related decision, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the right approach for your individual needs.
Bone Health
When it comes to bone health, calcium usually gets most of the attention.
However, magnesium is an unsung hero that plays a crucial role in maintaining strong, healthy bones. This essential mineral is a key player in bone formation, mineralization, and overall bone density.
We will examine how magnesium assists in maintaining a robust skeletal system.
First and foremost, magnesium is essential for the physiological functions of osteoblasts and osteoclasts, the cells responsible for bone formation and resorption.
These cells work tirelessly to maintain bone health, and magnesium ensures they’re performing at their best.
Additionally, magnesium affects bone development and mineralization by increasing the activity of phosphatase enzymes.
These enzymes are crucial for the proper formation of bone tissue, making magnesium an indispensable component of bone health.
Moreover, the combined effect of magnesium and vitamin D on bone health is significant, as they work together to enhance bone density and strength.
However, the contribution of magnesium to bone health extends beyond that. This mineral has an impact on the concentrations of parathyroid hormone and the active form of vitamin D. These are important regulators of bone homeostasis.
Magnesium can regulate parathyroid hormone signals through mediators like RANKL in osteocytes to affect bone remodeling.
This intricate interplay between magnesium and other bone-regulating hormones highlights its importance in maintaining overall bone health.
The consequences of magnesium deficiency on bone health can be significant. A lack of magnesium can lead to:
- Decreased bone mineral density.
- Increased risk of osteoporosis.
- Altered levels of parathyroid hormone and active vitamin D, inhibiting calcium absorption and inducing hypocalcemia.
This underscores the importance of maintaining adequate magnesium levels for optimal bone health.
Interestingly, combined magnesium and vitamin D therapy may be more effective in increasing serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations than vitamin D supplementation alone, suggesting a synergistic effect between these two essential nutrients in promoting bone health.
Blood Sugar Control
In the intricate world of metabolism, magnesium is a key element in maintaining healthy blood sugar levels.
This essential mineral is deeply involved in carbohydrate metabolism and insulin function, making it a key factor in blood sugar control.
We will discuss how magnesium assists in controlling blood sugar levels, a matter of particular importance for individuals at risk or those already living with diabetes.
Magnesium is necessary for healthy blood sugar regulation because it:
- is necessary for carbohydrate metabolism and insulin secretion, playing a crucial role in how the body processes carbohydrates and secretes insulin,
- acts as a co-factor for numerous enzymes involved in glucose utilization,
- and helps maintain optimal blood sugar levels, preventing dangerous spikes or drops.
By activating these enzymes, magnesium ensures that your body can effectively process and use the sugar in your bloodstream.
One of the most significant ways magnesium impacts blood sugar control is through its effect on insulin sensitivity.
Magnesium helps the body use protein and fat, control blood sugar, and reduce the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes by making the body better at using insulin.
It does this by promoting the efficient binding of insulin to cell receptors, allowing cells to respond more effectively to insulin’s signals.
This improved insulin sensitivity means that your body can more efficiently remove glucose from the bloodstream, keeping blood sugar levels stable.
The benefits of magnesium for blood sugar control are not just theoretical.
In studies, magnesium supplements were found to lower fasting blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity in individuals with diabetes or those at risk for the condition.
This suggests a potential benefit of magnesium supplementation for managing blood sugar levels.
This research provides compelling evidence for the potential of magnesium supplementation in managing and preventing diabetes, particularly in individuals with low magnesium levels.
Nevertheless, it is crucial to understand that the relationship between magnesium and diabetes is reciprocal.
Diabetes can lead to increased urinary excretion of magnesium, which exacerbates magnesium deficiency.
High blood sugar levels in diabetes can prompt the kidneys to eliminate excess glucose through urine, resulting in magnesium loss.
This creates a vicious cycle where diabetes leads to magnesium deficiency, which in turn makes blood sugar control more difficult.
For this reason, individuals with diabetes or at risk of diabetes should pay particular attention to their magnesium intake and consider regular monitoring of their magnesium levels.
Sleep Quality
In our rapidly evolving world, quality sleep is increasingly valuable.
Enter magnesium, nature’s own sleep aid. This essential mineral plays a crucial role in regulating our sleep patterns and promoting restful nights.
We will discuss how magnesium can contribute to improved sleep and why it could be worth incorporating it into your nightly routine.
The relationship between magnesium and sleep is significant, as magnesium can improve sleep quality by supporting various bodily functions.
Supplementing with magnesium at night could help improve sleep quality by controlling special brain chemicals linked to sleep.
One of these key brain chemicals is gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a neurotransmitter that plays a vital role in calming the nervous system.
Magnesium may help regulate GABA, which acts as a sedative to promote sleep. By enhancing GABA’s effects, magnesium can help quiet the mind and prepare the body for a restful night’s sleep.
Some benefits of supplementing with magnesium at night include:
- Improved sleep quality.
- Calming the nervous system.
- Promoting relaxation.
- Reducing anxiety and stress.
However, the sleep-enhancing benefits of magnesium extend further.
Studies have shown that magnesium deficiency is associated with decreased levels of melatonin, a hormone crucial for maintaining the circadian rhythm and promoting sleep.
Melatonin is often referred to as the “sleep hormone” because it helps regulate our sleep-wake cycle.
By supporting healthy melatonin production, magnesium helps ensure that our bodies are properly signaled when it’s time to wind down and prepare for sleep.
Beyond its effects on brain chemistry, magnesium also promotes sleep through its muscle-relaxing properties.
Magnesium can aid muscle relaxation by inhibiting the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor, contributing to improved relaxation and sleep. This muscle-relaxing effect can be particularly beneficial for those who experience tension or restlessness at bedtime.
By helping to ease physical tension, magnesium creates a more conducive environment for falling asleep and staying asleep throughout the night.
Stress and Anxiety Management
Given the high-stress nature of our modern world, discovering potent methods for managing anxiety and stress is essential to sustain overall well-being.
Enter magnesium, a mineral that’s gaining recognition for its potential to help calm the mind and soothe frazzled nerves.
We will discuss how this indispensable nutrient can be a significant asset in your stress management arsenal.
One of the primary ways magnesium helps manage stress is by regulating the body’s stress response.
Magnesium plays an important role in your body’s stress response, acting as a natural relaxant.
When we’re stressed, our bodies release cortisol, often referred to as the “stress hormone.”
Magnesium supplementation can lower stress hormone cortisol levels, which helps promote calmness and enhances sleep quality.
By keeping cortisol levels in check, magnesium can help prevent the physical and emotional symptoms associated with chronic stress. Some benefits of magnesium for stress management include:
- Regulating the body’s stress response.
- Acting as a natural relaxant.
- Lowering cortisol levels.
- Promoting calmness.
- Enhancing sleep quality.
Beyond its effects on cortisol, magnesium also impacts the brain in ways that can reduce anxiety.
Magnesium modulates neurotransmission, acting as an agonist for GABAA receptors, which are involved in the anxiolytic actions of benzodiazepines.
In simpler terms, this means that magnesium can help activate the same receptors in the brain that anti-anxiety medications target, potentially providing a natural way to promote relaxation and reduce anxiety symptoms.
The benefits of magnesium for mental health extend beyond just stress and anxiety management.
Getting enough magnesium from your diet or taking magnesium supplements can make a difference in preventing and managing mental health problems such as anxiety and depression.
It is important to consider this as part of your overall mental wellness strategy. This suggests that maintaining adequate magnesium levels could be an important factor in overall mental well-being.
Additionally, magnesium plays a role in promoting brain health by supporting the blood-brain barrier, which is crucial for protecting the brain from harmful substances.
Migraine Relief
For individuals struggling with migraines, discovering efficacious relief can be a taxing endeavor.
However, emerging research suggests that magnesium might be a promising ally in the fight against these debilitating headaches.
We will investigate how this essential mineral might offer relief for those afflicted with migraines.
Magnesium has been found to be potentially helpful in relieving headaches, particularly migraines. This mineral may offer relief for those experiencing these types of headaches.
This isn’t just anecdotal evidence; the scientific community has taken notice.
The American Headache Society gave magnesium a Level B rating for migraine prevention, indicating it is probably effective.
This endorsement from a respected medical organization underscores the potential of magnesium as a viable option for those seeking migraine relief.
But how exactly does magnesium work to prevent or alleviate migraines?
Magnesium may prevent a wave of brain signaling called cortical spreading depression, which is linked to migraine aura.
This neurological phenomenon is believed to be a key factor in the development of migraines, particularly those accompanied by aura.
By potentially interrupting this process, magnesium could help reduce the frequency and severity of migraine attacks.
Interestingly, the effectiveness of magnesium for migraines may vary depending on the type of migraine and the form of magnesium used. Daily oral magnesium can help prevent
Digestive Health
Magnesium and digestion hold a vital, albeit frequently undervalued, role in maintaining a healthy digestive system.
This essential mineral contributes to various aspects of digestive health, from nutrient absorption to bowel regularity.
We will examine how magnesium bolsters your digestive system and the significance of considering it for comprehensive gut health.
First and foremost, magnesium helps break down food and absorb nutrients. This fundamental process is essential for our bodies to:
- Extract the vitamins, minerals, and other beneficial compounds from the food we eat
- Facilitate efficient digestion and nutrient absorption
- Ensure that we’re getting the most out of our diet and supporting overall health.
Another key way magnesium supports digestive health is through its effect on the muscles in the digestive tract.
Magnesium acts as a muscle relaxant, impacting the digestive tract. This relaxation effect can be particularly beneficial for those who experience digestive discomfort or irregularity.
Magnesium helps prevent constipation by relaxing stomach muscles, allowing for smoother, more comfortable bowel movements.
If you are struggling with constipation, magnesium can be a natural solution.
Magnesium citrate, a specific form of magnesium, pulls extra water into the intestines, aiding in constipation relief.
Magnesium supplements may promote regular bowel movements and have a laxative effect. This gentle laxative action can be a safer alternative to harsh chemical laxatives for many people dealing with occasional constipation.
However, it’s important to note that the relationship between magnesium and digestive health is a two-way street.
Gastrointestinal diseases like Crohn’s disease and gluten-sensitive enteropathy can lead to magnesium depletion due to chronic diarrhea and fat malabsorption. This highlights the importance of maintaining adequate magnesium levels, especially for those with digestive disorders.
If you have a gastrointestinal condition, it may be worth discussing your magnesium status with a healthcare provider to ensure you’re not at risk for deficiency.
Muscle Function
In ensuring our bodies move smoothly and efficiently, magnesium takes on a vital role behind the scenes. This essential mineral is crucial for proper muscle function, affecting everything from daily movements to athletic performance.
We will delve into how magnesium aids our muscles and the importance of maintaining sufficient levels.
Magnesium helps muscles contract with more force and relax effectively, which is essential for overall muscle function. This dual action of supporting both contraction and relaxation is what makes magnesium so vital for muscle health.
When our muscles contract, magnesium helps to regulate the influx of calcium into muscle cells, allowing for stronger, more efficient contractions.
Then, when it’s time for muscles to relax, magnesium helps to remove calcium from the cells, enabling smooth and complete relaxation.
The importance of magnesium for muscle health becomes even more apparent when we consider the consequences of deficiency.
A deficiency in magnesium is linked to more frequent muscle cramps and injuries, emphasizing its preventive role.
If you’ve ever experienced the sudden, intense pain of a muscle cramp, you know how disruptive they can be.
By ensuring adequate magnesium intake, you may be able to reduce the frequency and severity of these uncomfortable muscle spasms.
Magnesium and muscle cramps are closely related, as magnesium can help reduce the frequency and severity of muscle cramps.
Beyond preventing cramps and injuries, magnesium also plays a crucial role in muscle recovery and performance.
Magnesium aids in muscle relaxation and recovery after strain and is commonly used in Epsom salts for muscle relief. This is why many athletes and fitness enthusiasts turn to magnesium-rich Epsom salt baths after intense workouts. But the benefits don’t stop there.
Supplementing with magnesium can improve athletic performance by enhancing strength and endurance.
Whether you’re a professional athlete or just someone looking to improve your fitness, ensuring adequate magnesium intake could give you the edge you need to reach your goals.
Inflammation Reduction
Inflammation is a focal discussion point in health circles, and rightly so.
Chronic inflammation has been linked to a host of health issues, from heart disease to cancer.
But did you know that magnesium and inflammation are closely related, and magnesium could play a role in keeping inflammation in check?
We will investigate how this key mineral could potentially assist in reducing inflammation and promoting overall health.
Magnesium has shown anti-inflammatory properties, which are beneficial for individuals with diabetes where chronic inflammation is a contributing factor.
This is particularly important because inflammation and diabetes often go hand in hand, creating a vicious cycle that can be difficult to break.
By helping to reduce inflammation, magnesium may not only alleviate symptoms but also potentially reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
One way magnesium may help reduce inflammation is through its effects on body composition.
Magnesium can affect inflammation by potentially altering body composition, such as reducing fat mass.
Excess body fat, particularly visceral fat, is known to produce inflammatory compounds.
By potentially helping to reduce fat mass, magnesium could indirectly contribute to lower levels of inflammation in the body.
At a cellular level, magnesium’s anti-inflammatory effects may be linked to its role in regulating calcium.
Magnesium may modulate inflammation by influencing intracellular calcium levels.
Calcium plays a crucial role in the inflammatory response, and by helping to regulate calcium levels within cells, magnesium may help keep inflammation in check.
But the evidence for magnesium’s anti-inflammatory effects isn’t just theoretical.
Research has shown measurable impacts on inflammatory markers.
Magnesium supplementation can significantly reduce plasma fibrinogen levels, which is an inflammatory marker, by about 9 percent.
Additionally, there is a significant inverse correlation between serum magnesium and high-sensitive C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) levels, with low serum magnesium concentrations linked to elevated C-reactive protein (CRP) levels.
CRP is a widely used marker of inflammation, and these findings suggest that maintaining adequate magnesium levels could help keep inflammation under control.
Sources of Magnesium

Having examined the numerous health benefits of magnesium, you may be curious about how to guarantee an adequate intake of this essential mineral in your diet.
The good news is that magnesium is widely available in a variety of foods, and with a little knowledge, you can easily boost your intake.
We will investigate the plentiful sources of magnesium and how you can integrate them into your everyday diet.
Magnesium is widely distributed in both plant and animal foods, including green leafy vegetables, legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains.
Foods high in dietary fiber are a good source of magnesium. These foods can help meet your magnesium needs as part of a balanced diet. This means that by focusing on a diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods, you’re likely already getting a good amount of magnesium.
Some of the best sources include spinach, Swiss chard, and other leafy greens, as well as pumpkin seeds, almonds, and black beans.
For those who enjoy grains, there’s more good news.
Some breakfast cereals and other foods are fortified with magnesium. This means that even if you’re not always able to eat a wide variety of whole foods, you can still boost your magnesium intake through fortified options.
However, it’s important to read labels carefully, as not all fortified foods are created equal in terms of their nutritional value.
Interestingly, your drinking water can also be a source of magnesium.
Tap, mineral, and bottled waters can be sources of magnesium, with content varying by source and brand.
While the amount of magnesium in water is generally not enough to meet your daily needs on its own, it can contribute to your overall intake.
If you’re curious about the magnesium content of your local water supply, you can usually find this information from your local water authority.
When it comes to how much magnesium you need, the recommended magnesium intake for most people falls within the 300-400 mg/day range.
It’s worth noting that approximately 30% to 40% of dietary magnesium is absorbed by the body, which is why it’s important to consume magnesium-rich foods regularly.
By incorporating a variety of magnesium-rich foods into your diet, you can help ensure that your body has the magnesium it needs to support optimal health.
Some examples of magnesium-rich foods include:
- Spinach
- Almonds
- Avocado
- Black beans
- Quinoa
- Dark chocolate
Adding these foods to your meals and snacks can help you meet your daily magnesium needs.
Types of Magnesium Supplements
Although it is ideal to get magnesium from food sources, supplements can sometimes be advantageous, particularly if you are at risk of deficiency.
However, not all magnesium supplements are created equal. Different forms of magnesium have varying absorption rates and potential benefits.
We will examine the available types of magnesium supplements and how to select the most suitable one for your requirements.
Magnesium supplements are available in forms such as magnesium oxide, citrate, and chloride.
Each of these forms has different properties that can affect how well they’re absorbed by the body and what specific benefits they might offer.
Forms of magnesium that dissolve well in liquid are typically more completely absorbed. This is an important consideration when choosing a supplement, as better absorption means your body can make better use of the magnesium you’re taking.
Among the various forms of magnesium supplements, some stand out for their high bioavailability.
Oral magnesium supplementation in forms that are well-absorbed in the gut include:
- Aspartate
- Citrate
- Lactate
- Chloride
Magnesium lactate and magnesium malate are highly bioavailable and easy to absorb. These forms might be particularly beneficial for those looking to increase their magnesium levels efficiently.
For those dealing with specific health concerns, certain forms of magnesium might be more appropriate.
Magnesium citrate is often used for treating constipation and is easier for the body to absorb than other forms.
If you’re looking for a supplement to help with digestive issues, this might be a good option to consider.
Magnesium glycinate is well-tolerated and causes minimal side effects, making it a good choice for those who experience gastrointestinal upset with other forms of magnesium.
It’s worth noting that magnesium can be absorbed through the skin as well as taken orally.
Magnesium chloride can be absorbed through the skin, though the amount absorbed is small. This has led to the popularity of magnesium oils and bath salts, which some people find helpful for muscle relaxation and sleep.
However, magnesium oxide, while commonly used for treating constipation or as an antacid, is poorly absorbed. This means it might not be the best choice if you’re looking to increase your overall magnesium levels.
Magnesium 7: A Comprehensive Approach to Magnesium Supplementation
If you are seeking to maximize your magnesium advantages in your health regimen, a full-spectrum magnesium supplement like Magnesium 7 offers a comprehensive approach.
This type of supplement combines seven different forms of elemental magnesium, each with its own specific benefits, along with important co-factors for enhanced absorption.
The seven forms of magnesium included are:
- Magnesium Chelate for muscle recovery
- Magnesium Glycinate for sleep, anxiety, and brain health
- Magnesium Aspartate for mood and mental well-being
- Magnesium Malate for brain and nervous system support
- Magnesium Orotate for heart health and exercise performance
- Magnesium Taurate for blood pressure management and relaxation
- Magnesium Citrate for cardiovascular and intestinal health
This diverse combination aims to provide a wide range of magnesium’s benefits, from stress reduction and improved sleep to supporting heart health, bone strength, and muscle function.
The inclusion of Vitamin B6 and Manganese Citrate as co-factors may further enhance the supplement’s effectiveness, particularly in stress reduction and bone health.
It’s worth noting that this type of supplement often avoids less bioavailable forms of magnesium like magnesium oxide or sulfate, focusing instead on more easily absorbed forms.
However, as with any supplement, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before adding it to your routine, especially if you have any existing health conditions or are taking medications.
While a balanced diet rich in magnesium-containing foods should be the primary source of this essential mineral, a full-spectrum supplement like Magnesium 7 could be a useful addition for those looking to ensure they’re receiving a comprehensive range of magnesium’s benefits.
Potential Side Effects of Excess Magnesium
While magnesium is indispensable for numerous bodily functions, it is crucial to bear in mind that an excess can sometimes be detrimental.
Understanding the potential side effects of excess magnesium intake is crucial for anyone considering magnesium supplementation.
We will investigate the consequences of excessive magnesium consumption and how to avoid such instances.
High doses of magnesium from supplements often result in diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal cramping.
These gastrointestinal side effects are typically the first signs that you might be taking too much magnesium.
Gastrointestinal side effects are common with magnesium supplements, but they can often be managed.
One can manage gastrointestinal side effects from magnesium supplements by changing the form of magnesium or cutting back the dose.
If you’re experiencing these symptoms, it’s worth discussing with your healthcare provider to find the right balance.
In rare cases, excessive magnesium intake can lead to more serious issues. Very large doses of magnesium-containing laxatives or antacids can lead to magnesium toxicity.
Hypermagnesemia is a condition where there is too much magnesium in the blood. Symptoms of hypermagnesemia can include:
- Digestive issues
- Respiratory distress
- Low blood pressure
- Irregular heartbeat
These symptoms can indicate an overdose of magnesium in the body. These severe symptoms are typically only seen with extremely high doses of magnesium, often in individuals with impaired kidney function.
It’s important to note that for most healthy adults, the risk of magnesium toxicity from dietary sources is very low.
For healthy adults, the risk of experiencing a magnesium overdose is extremely low. However, certain groups may be at higher risk.
The risk of magnesium overdose is higher in individuals with chronic kidney disease.
People with heart disease and gastrointestinal disorders are at increased risk when taking magnesium supplements.
If you fall into any of these categories, it’s crucial to consult with your healthcare provider before starting any magnesium supplementation.
To help prevent excessive magnesium intake, regulatory bodies have established guidelines for safe consumption.
The Tolerable Upper Intake Level (UL) for magnesium set by the Food and Nutrition Board is 350 milligrams per day.
For most adults, the maximum dietary allowance is typically around 400 mg or less. This is an important guideline to keep in mind when planning your daily intake.
Doses less than 350 mg daily are considered safe for most adults when taken by mouth. It’s important to note that these upper limits apply to supplemental magnesium, not magnesium from food sources.
Taking a magnesium supplement every day likely isn’t unsafe for most people, but it’s important to not take too much.
Always follow the recommended dosage on the supplement label or as advised by your healthcare provider.
Interactions with Medications
While magnesium is typically safe and advantageous for most individuals, it is crucial to note that it can interact with certain medications.
These interactions can either enhance or reduce the effectiveness of the medications, or in some cases, lead to adverse effects.
We will examine some key drug interactions to be aware of if you’re contemplating magnesium supplementation.
One of the most significant interactions occurs with magnesium and antibiotics.
Magnesium can reduce the absorption of quinolone and tetracycline antibiotics, such as ciprofloxacin and doxycycline. This means that if you’re taking these types of antibiotics, you should avoid taking magnesium supplements at the same time.
It’s generally recommended to space out the intake of these medications and magnesium supplements by at least 2-3 hours. In some cases, the interaction can be even more serious.
Concurrent use of magnesium and aminoglycoside antibiotics may cause neuromuscular weakness and paralysis.
If you’re prescribed any antibiotics, it’s crucial to inform your healthcare provider about any magnesium supplements you’re taking.
Magnesium can also interact with medications used to treat various chronic conditions.
Diuretics like furosemide and hydrochlorothiazide can lower magnesium levels in the body. This means that if you’re taking these medications, you might need to pay extra attention to your magnesium intake.
On the other hand, magnesium supplements may increase the absorption of certain diabetes medications like glipizide.
While this might seem beneficial, it’s important to monitor blood sugar levels closely as it could potentially lead to hypoglycemia.
Heart medications are another category where magnesium interactions can occur.
Calcium channel blockers, particularly nifedipine, may have increased side effects when taken with magnesium. This interaction could potentially lead to excessive blood pressure lowering.
Additionally, magnesium-containing antacids can reduce the effectiveness of levothyroxine, a medication for underactive thyroid.
If you’re taking any of these medications, it’s essential to discuss magnesium supplementation with your healthcare provider.
Given the potential for these interactions, it’s crucial to be proactive about your health. If considering a magnesium supplement while taking other medications, it is important to:
- Inform the doctor about all the other medicines being taken and to check for possible interactions.
- Discuss starting a magnesium supplement with their primary-care doctor and review their health history and medications.
- Doctors may conduct a magnesium blood test if concerned about magnesium levels.
By being open and transparent with your healthcare provider, you can ensure that you’re getting the benefits of magnesium without risking harmful interactions with your medications.
Summary
Magnesium is a vital mineral with wide-ranging health benefits, from supporting heart and bone health to regulating blood sugar and improving sleep quality.
It also plays crucial roles in stress management, muscle function, and reducing inflammation. While a balanced diet is the primary source of magnesium, some may benefit from supplementation.
To maximize these magnesium advantages, consider incorporating a full-spectrum magnesium supplement into your daily routine.
These comprehensive formulations combine multiple forms of magnesium to potentially offer a broader range of benefits.
However, always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen, especially if you have existing health conditions or take medications.
Take action today: Explore full-spectrum magnesium supplements and discover how this essential mineral could enhance your overall health and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the use and benefits of magnesium?
Make sure to include magnesium in your diet as it is essential for healthy muscles, nerves, bones, and blood sugar levels, and helps reduce the risk of health issues like heart attack, stroke, diabetes, or osteoporosis.
How much magnesium should I take daily?
For most adults, the recommended daily intake of magnesium is 300-400 mg, but it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice.
Can I get enough magnesium from my diet alone?
Yes, you can get enough magnesium from a balanced diet, but some people may need supplements depending on their health conditions or medications.
What are the signs of magnesium deficiency?
If you’re experiencing muscle cramps, fatigue, irritability, poor sleep, or irregular heartbeat, you might be deficient in magnesium. It’s best to consult with a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis.
Is it safe to take magnesium supplements every day?
Yes, for most healthy adults, taking magnesium supplements every day is safe as long as you stay within the recommended dosage. It’s always a good idea to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement routine.
Magnesium Anxiety Relief: Exploring Its Potential for Inner PeaceAre anxiety and stress overwhelming your daily life? Discover the potential of magnesium anxiety relief—a natural approach that’s gaining attention. This essential mineral could be the key to calming your mind and easing your worries.
Magnesium plays a crucial role in regulating neurotransmitters and stress hormones, directly impacting our ability to cope with anxiety. But how effective is it really, and what’s the science behind it?
From magnesium glycinate to L-threonate, various forms of this supplement offer unique benefits for mental well-being. This guide explores the research, recommended dosages, and what you need to know to potentially harness the power of magnesium for a more relaxed, balanced life.
Ready to take control of your anxiety? Read on about magnesium and its promising effects on stress management.
Key Takeaways
- Magnesium can help reduce anxiety by regulating neurotransmitters, controlling cortisol levels, improving sleep quality, and relaxing muscles.
- The best forms of magnesium for anxiety are magnesium glycinate, magnesium L-threonate, and magnesium taurate due to their high absorption rates and calming effects.
- Some supplements combine multiple forms of magnesium, such as Magnesium 7, which includes seven different types to potentially address various aspects of health and anxiety.
- It’s important to consult a healthcare provider before starting magnesium supplements to determine the right dosage and avoid potential side effects or drug interactions.
How Magnesium Affects Anxiety

Magnesium assists in anxiety reduction by:
- Moderating cortisol levels.
- Harmonizing neurotransmitters in the brain.
- Improving sleep quality.
- Calming the nervous system.
- Improving mood.
- Decreasing muscle tension.
Magnesium interacts with the stress response system to help manage anxiety. It curtails or obstructs neuroendocrine pathways that facilitate cortisol access to the brain.
All of these factors could contribute to reducing anxiety symptoms, including mild anxiety.
However, the evidence remains mixed; while some studies report positive effects of magnesium intake on anxiety outcomes, more research is needed to confirm its effectiveness.
There is a well-established connection between magnesium deficiency and anxiety. This suggests that supplementing with magnesium may be beneficial for individuals with anxiety.
The mechanisms behind this potential benefit are multifaceted, involving the regulation of neurotransmitters, control of stress hormones like cortisol, and muscle relaxation.
Regulating Neurotransmitters
Magnesium plays a crucial role in controlling neurotransmitters critical to mood and the regulation of anxiety, such as GABA and glutamate.
While GABA acts as an inhibitory neurotransmitter that decreases neural activity leading to a calming effect by interacting with GABA receptors, glutamate operates as the primary excitatory neurotransmitter which can amplify anxiety when not adequately controlled.
By curbing the release of glutamate and boosting GABA function, magnesium contributes to maintaining these neurotransmitters’ equilibrium, possibly lessening symptoms associated with anxiety.
Achieving this balance is vital for preserving brain health and minimizing susceptibility to disorders related to anxiety.
Cortisol Control
Magnesium plays a critical role in balancing cortisol, often known as the “stress hormone,” within the body’s stress response system.
When facing chronic stress, which has been linked to exacerbated anxiety and depression symptoms, magnesium aids in stabilizing cortisol concentrations.
It mitigates extreme anxiety by curtailing or obstructing neuroendocrine pathways that facilitate cortisol access to the brain, thus helping relieve escalated levels of stress.
Magnesium also affects the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis to help manage stress and anxiety.
The beneficial effects of magnesium on our body’s capacity to handle stress include:
- Adjusting the activity of the hypothalamus for better regulation of cortisol.
- Serving as a controlling force within the stress response mechanism.
- Noticeably diminishing chronic stress’s role in heightening anxiety-related issues.
Essentially, through these processes involving neurological and endocrine systems interactions with our psychological state—specifically via regulating neurotransmission and hormonal balance—magnesium is instrumental in reducing intense responses provoked by sustained periods of pressure or strain (chronic stresses).
This modulation is key for maintaining mental well-being and tempering heightened sensations related specifically to worry or despair (anxiety or depression).
Muscle Relaxation

Magnesium contributes to both muscle and nerve function, which could alleviate physical manifestations of anxiety such as muscle tension.
Its involvement in the contraction and relaxation of muscles, including the heart muscles, may lead to a soothing impact.
The use of magnesium supplementation can also be advantageous for issues like restless leg syndrome and muscular spasms that interfere with restful sleep and raise stress levels.
Through fostering muscle relaxation, magnesium aids in mitigating symptoms that might aggravate anxiety, thus enhancing an overall feeling of tranquility.
Best Forms of Magnesium for Anxiety
Different forms of magnesium supplements offer unique benefits, and they are not all identical in their effects.
Recommended for easing anxiety, options such as magnesium glycinate, magnesium L-threonate, and magnesium taurate are among the various kinds available that cater to distinct requirements and tastes.
A deeper exploration into the advantages of these particular types of magnesium will assist you in choosing which form aligns best with your personal lifestyle and health needs.
Magnesium Glycinate
Magnesium glycinate is frequently recommended for anxiety because it has a superior absorption rate that enhances its ability to alleviate stress.
This particular form of magnesium is also gentle on the gastrointestinal system, which makes it popular among individuals seeking supplementation.
Other forms of magnesium used for this purpose include magnesium malate and magnesium oxide.
The presence of glycine in magnesium glycinate imparts an additional calming effect on the brain, which helps to calm the brain.
In reducing anxiety. When addressing anxiety and various mental health conditions, the efficacy of magnesium glycinate stands out due to these properties.
Magnesium L-Threonate
Magnesium L-threonate is recognized for its effectiveness as it has the unique ability to:
- Traverse the blood-brain barrier, thus enhancing magnesium levels within the brain.
- Bolster cognitive function and promote mental clarity.
- Engage with receptors that influence mood, cognitive functions, and manage stress response.
This amino acid variant exhibits high absorption rates and presents a multitude of benefits dedicated to preserving brain health.
By boosting magnesium concentrations in the brain, magnesium L-threonate plays a significant role in supporting overall brain health and reducing anxiety levels.
Magnesium Taurate
Combining magnesium with taurine, magnesium taurate is recognized for its potential to provide anxiety relief through its calming properties. Notable features of this form include:
- Its soothing effects.
- Protection for neural pathways.
- Reduction in inflammation.
- Enhanced ability to transport magnesium into the brain.
- A mild influence on digestive health.
Despite the need for studies to comprehensively ascertain the impact of magnesium taurate on human anxiety, these promising advantages suggest it’s a variant worthy of attention.
Magnesium 7: A Comprehensive Magnesium Blend
If you are seeking a multi-faceted approach to magnesium supplementation, Magnesium 7 offers a unique combination of seven elemental magnesium forms. This full-spectrum supplement includes:
- Magnesium Chelate (muscle recovery)
- Magnesium Glycinate (sleep, anxiety, brain health)
- Magnesium Aspartate (mood support)
- Magnesium Malate (nervous system health)
- Magnesium Orotate (heart health, exercise performance)
- Magnesium Taurate (relaxation, blood pressure)
- Magnesium Citrate (cardiovascular, intestinal health)
With 250mg of magnesium per capsule and added co-factors like Vitamin B6 and Manganese Citrate, Magnesium 7 aims to provide comprehensive benefits. These may include stress reduction, improved sleep, heart and bone support, and enhanced nutrient absorption.
The supplement uses chelated forms for better bioavailability and excludes less absorbable types like magnesium oxide or sulfate.
While this all-in-one approach is intriguing, individual responses to magnesium supplements can vary.
As with any new supplement regimen, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider before starting, especially if you have existing health conditions or take medications.
Ready to explore the potential benefits of a comprehensive magnesium supplement? Consider discussing Magnesium 7 with your healthcare provider to determine if it’s the right choice for your wellness journey.
Remember, supplements should complement, not replace, a balanced, magnesium-rich diet.
How Much Magnesium Should You Take?
The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for magnesium differs based on one’s sex, age, and unique health conditions.
Adult RDA ranges from 310 to 420 mg, contingent upon the individual’s gender and stage of life.
The RDA for magnesium varies: for men aged 19-30, it is 400 mg, and for women of the same age, it is 310 mg. For those over 31, men require 420 mg, while women need 320 mg.
In light of the absence of a universally established dose tailored specifically to mitigate anxiety symptoms, it is crucial to seek advice from a medical professional who can recommend an appropriate dosage that suits your specific needs.
Recommended Dietary Allowance
For adults, the recommended dietary allowance (RDA) of magnesium varies between 310 and 420 mg based on one’s age and sex.
Males aged 19 to 30 should consume 400 mg, whereas females in this age group need 310 mg.
For individuals older than 31, the RDA goes up to 420 mg for males and rises slightly to a requirement of 320 mg for females.
Dosage for Anxiety Relief
Research examining the anti-anxiety properties of magnesium typically employs daily doses between 75 and 360 mg.
The precise amount is determined by variables including health conditions, as well as the individual’s age and gender, underscoring the need for personalized recommendations.
Consulting a Healthcare Provider
It is recommended to seek the guidance of a healthcare practitioner before initiating any regimen with magnesium supplements to ensure you receive advice tailored to your unique health conditions and requirements regarding the appropriate dosage and form.
If considering exceeding the recommended daily allowance for magnesium supplement intake or if planning to take these supplements in conjunction with other medications, it’s crucial to discuss this with a doctor first.
Doing so helps prevent unwanted interactions and side effects.
Dietary Sources of Magnesium

Incorporating foods such as nuts, seeds, leafy greens, and whole grains into your diet is essential for enhancing your magnesium intake.
Dietary magnesium is crucial for various bodily functions and can be obtained from these natural food sources. These natural dietary options contribute to an increase in this vital nutrient, promoting general health.
To elevate your magnesium levels through diet effectively, consider these top food sources rich in magnesium.
Leafy Greens
Leafy vegetables like kale and spinach are packed with essential nutrients, including magnesium. They also deliver a wealth of other beneficial components such as iron, vitamins A, C, and K.
Specifically focusing on spinach, it is notably high in magnesium content. For example, consuming just one cup of boiled spinach offers 157 mg of this important mineral.
Nuts and Seeds
An essential mineral, magnesium, is crucial for numerous body functions and may aid in reducing anxiety. It can be found abundantly in nuts and seeds.
For instance, one ounce of almonds contains roughly 76 mg of magnesium.
Cashews provide about 83 mg per ounce, while an equal serving of pumpkin seeds boasts a notable 168 mg.
Whole Grains
Whole grains play a crucial role as a dietary source of magnesium, an essential mineral for daily intake.
A nutrient-packed option such as cooked quinoa delivers 118 mg of magnesium per cup, highlighting its substantial contribution to our nutritional needs.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
Taking magnesium supplements is typically safe for most adults, but it’s important to be cognizant of possible side effects.
Among the prevalent concerns are gastrointestinal complications, the risk of magnesium toxicity, and potential interactions with medications.
Magnesium toxicity can lead to serious health issues, but it can be avoided by adhering to recommended dosages and consulting with a healthcare provider.
Before embarking on a regimen involving new dietary supplements, seeking guidance from a healthcare professional can help prevent any negative outcomes.
This precautionary measure ensures that one steers clear of adverse effects associated with supplement use.
Gastrointestinal Issues
Typical adverse reactions to magnesium supplementation can consist of:
- Stomach pain.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Diarrhea, which is more prevalent with varieties such as magnesium citrate.
These issues arise when excessively large doses result in an intake of too much magnesium.
Magnesium Toxicity
Manifestations of magnesium toxicity can involve an arrhythmia and diminished blood pressure.
In extreme instances, this condition may progress to reduced respiration, unconsciousness, and potentially be fatal.
Drug Interactions
Taking magnesium supplements could potentially interfere with how some medicines work, making them less effective.
This includes a reduced uptake of antibiotics and diminishing the impact of digoxin, which is prescribed for heart-related issues.
It is imperative to seek advice from a healthcare professional before commencing any new regimen that includes dietary supplements in order to prevent unwanted interactions and adverse reactions.
Additional Benefits of Magnesium
Magnesium confers numerous other advantages aside from diminishing anxiety. This vital nutrient aids in more than 300 enzyme-driven processes within the body, including:
- DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis,
- blood sugar level control,
- blood pressure regulation,
- heart rhythm modulation,
- immune system enhancement,
- and muscle function support.
Magnesium supports the immune system and contributes to overall health.
Let’s delve deeper into a selection of these additional health benefits provided by magnesium.
Improved Sleep Quality
By soothing the nervous system, easing muscle tension, and aiding in melatonin production, magnesium helps enhance sleep.
Taking magnesium supplements could shorten the amount of time needed to fall asleep while potentially enhancing both the quality and length of sleep.
Blood Sugar Control
Magnesium is integral to the regulation of blood glucose levels, and it has been observed that nearly half (48%) of individuals with type 2 diabetes exhibit decreased magnesium levels, which could negatively affect their ability to manage blood sugar.
By improving insulin sensitivity, a crucial aspect in the control of blood sugar, taking magnesium supplements may offer beneficial effects.
Cardiovascular Health
Taking magnesium supplements may aid in decreasing blood pressure, thereby diminishing the likelihood of heart disease.
An increased consumption of magnesium is associated with a reduced risk of cardiovascular diseases such as stroke and high blood pressure.
As an essential mineral, it contributes to the well-being of the cardiovascular system by ensuring steady heart rhythms, fostering relaxation within blood vessels, and facilitating energy production.
Through its capacity to lower inflammation and oxidative stress levels in the body (factors often linked with cardiac issues), magnesium plays a substantial role in reinforcing overall cardiovascular health.
These effects underscore how integrating this key nutrient into one’s diet can not only lessen chances for developing cardiovascular conditions, but also enhance mental health outcomes.
Summary
Magnesium’s potential to alleviate anxiety is supported by its ability to regulate neurotransmitters, control cortisol levels, and promote muscle relaxation.
While more research is needed to confirm its effectiveness fully, the current evidence suggests that magnesium supplementation could be a valuable tool in reducing anxiety symptoms.
Incorporating magnesium into your diet through natural sources like leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and whole grains, or considering supplements such as magnesium glycinate, L-threonate, or taurate, can provide additional health benefits.
Some supplements, like Magnesium 7, combine multiple forms of magnesium to potentially address various aspects of health. However, it’s important to approach such options with a critical eye and consult with a healthcare provider.
Always consult a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dosage and form for your specific needs.
With magnesium’s myriad benefits, it might just be the key to helping you stress less and live a healthier, more balanced life.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can magnesium really help reduce anxiety?
Magnesium has the ability to mitigate anxiety through the regulation of neurotransmitters, management of cortisol levels, and facilitation of muscle relaxation.
Additional research is required to comprehensively ascertain its effects.
What is the best form of magnesium for anxiety?
Magnesium glycinate, L-threonate, and taurate are considered the most effective types of magnesium for alleviating anxiety due to their superior absorption capabilities and tranquilizing properties.
Experiment with each form to determine which one offers you optimal results!
How much magnesium should I take for anxiety relief?
Speak with a healthcare provider to ascertain the appropriate dosage of magnesium for alleviating anxiety, considering that research studies have employed dosages varying from 75 mg to 360 mg daily.
Are there any side effects of taking magnesium supplements?
Certainly, when you take magnesium supplements, it’s important to be mindful of the possibility that they can induce gastrointestinal problems such as diarrhea and nausea.
Ingestion of high doses might result in magnesium toxicity, a serious condition necessitating medical intervention.
To prevent these adverse consequences, monitor your intake of magnesium carefully while taking these supplements.
Can I get enough magnesium from my diet alone?
Certainly, by incorporating leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and whole grains into your diet, it’s possible to obtain sufficient magnesium.
Nevertheless, some people might still require supplementation to fulfill their dietary requirements for this mineral.

